RabGEFs are a major determinant for specific Rab membrane targeting
- PMID: 23382462
- PMCID: PMC3563681
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201209113
RabGEFs are a major determinant for specific Rab membrane targeting
Abstract
Eukaryotic cells critically depend on the correct regulation of intracellular vesicular trafficking to transport biological material. The Rab subfamily of small guanosine triphosphatases controls these processes by acting as a molecular on/off switch. To fulfill their function, active Rab proteins need to localize to intracellular membranes via posttranslationally attached geranylgeranyl lipids. Each member of the manifold Rab family localizes specifically to a distinct membrane, but it is unclear how this specific membrane recruitment is achieved. Here, we demonstrate that Rab-activating guanosine diphosphate/guanosine triphosphate exchange factors (GEFs) display the minimal targeting machinery for recruiting Rabs from the cytosol to the correct membrane using the Rab-GEF pairs Rab5A-Rabex-5, Rab1A-DrrA, and Rab8-Rabin8 as model systems. Specific mistargeting of Rabex-5/DrrA/Rabin8 to mitochondria led to catalytic recruitment of Rab5A/Rab1A/Rab8A in a time-dependent manner that required the catalytic activity of the GEF. Therefore, RabGEFs are major determinants for specific Rab membrane targeting.
Figures
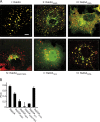


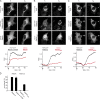

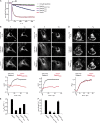
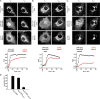


References
-
- Adler J., Parmryd I. 2010. Quantifying colocalization by correlation: the Pearson correlation coefficient is superior to the Mander’s overlap coefficient. Cytometry A. 77:733–742 - PubMed
-
- Allaire P.D., Ritter B., Thomas S., Burman J.L., Denisov A.Y., Legendre-Guillemin V., Harper S.Q., Davidson B.L., Gehring K., McPherson P.S. 2006. Connecdenn, a novel DENN domain-containing protein of neuronal clathrin-coated vesicles functioning in synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J. Neurosci. 26:13202–13212 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4608-06.2006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

