Neuropeptide Y receptors: how to get subtype selectivity
- PMID: 23382728
- PMCID: PMC3563083
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00005
Neuropeptide Y receptors: how to get subtype selectivity
Abstract
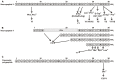
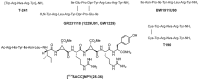
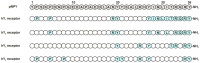
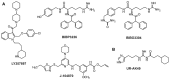
The neuropeptide Y (NPY) system is a multireceptor/multiligand system consisting of four receptors in humans (hY(1), hY(2), hY(4), hY(5)) and three agonists (NPY, PYY, PP) that activate these receptors with different potency. The relevance of this system in diseases like obesity or cancer, and the different role that each receptor plays influencing different biological processes makes this system suitable for the design of subtype selectivity studies. In this review we focus on the latest findings within the NPY system, we summarize recent mutagenesis studies, structure activity relationship studies, receptor chimera, and selective ligands focusing also on the binding mode of the native agonists.
Keywords: GPCR; NPY; YR; ligand side; receptor side; subtype selectivity.
Figures

References
-
- Akerberg H., Fallmar H., Sjodin P., Boukharta L., Gutierrez-De-Teran H., Lundell I., et al. (2010). Mutagenesis of human neuropeptide Y/peptide YY receptor Y2 reveals additional differences to Y1 in interactions with highly conserved ligand positions. Regul. Pept. 163 120–129 - PubMed
-
- Antal-Zimanyi I., Bruce M. A., Leboulluec K. L., Iben L. G., Mattson G. K., Mcgovern R. T., et al. (2008). Pharmacological characterization and appetite suppressive properties of BMS-193885, a novel and selective neuropeptide Y(1) receptor antagonist. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 590 224–232 - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A., Inui A., Ueno N., Fujimiya M., Fujino M. A., Kasuga M. (1999). Mouse pancreatic polypeptide modulates food intake, while not influencing anxiety in mice. Peptides 20 1445–1448 - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A., Inui A., Yuzuriha H., Ueno N., Katsuura G., Fujimiya M., et al. (2003). Characterization of the effects of pancreatic polypeptide in the regulation of energy balance. Gastroenterology 124 1325–1336 - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniam A. (2002). Clinical potentials of neuropeptide Y family of hormones. Am. J. Surg. 183 430–434 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

