The phosphoinositide-binding protein ZF21 regulates ECM degradation by invadopodia
- PMID: 23382803
- PMCID: PMC3561396
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050825
The phosphoinositide-binding protein ZF21 regulates ECM degradation by invadopodia
Abstract
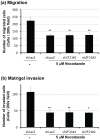
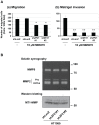
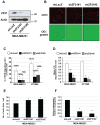
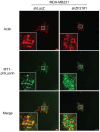
During the process of tumor invasion, cells require footholds on extracellular matrices (ECM) that are created by forming focal adhesions (FAs) using integrins. On the other hand, cells must degrade the ECM barrier using extracellular proteases including MMPs in the direction of cell movement. Degradation occurs at the leading edges or invadopodia of cells, which are enriched in proteases and adhesion molecules. Recently, we showed that the phosphoinositide-binding protein ZF21 regulates FA disassembly. ZF21 increased cell migration by promoting the turnover of FAs. In addition, ZF21 promotes experimental tumor metastasis to lung in mice and its depletion suppresses it. However, it is not known whether ZF21 regulates cancer cell invasion in addition to its activity on FAs. In this study, we demonstrate that ZF21 also regulates invasion of tumor cells, whereas it does not affect the overall production of MMP-2, MMP-9, and MT1-MMP by the cells. Also, we observe that the ECM-degrading activity specifically at the invadopodia is severely abrogated. In the ZF21 depleted cells MT1-MMP cannot accumulate to the invadopodia and thereby cannot contribute to the ECM degradation. Thus, this study demonstrates that ZF21 is a key player regulating multiple aspects of cancer cell migration and invasion. Possible mechanisms regulating ECM degradation at the invadopodia are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Gupta GP, Massague J (2006) Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127: 679–695. - PubMed
-
- Steeg PS (2006) Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med 12: 895–904. - PubMed
-
- Guo W, Giancotti FG (2004) Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 816–826. - PubMed
-
- Petit V, Thiery JP (2000) Focal adhesions: structure and dynamics. Biol Cell 92: 477–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

