MicroRNA-195 inhibits the proliferation of human glioma cells by directly targeting cyclin D1 and cyclin E1
- PMID: 23383003
- PMCID: PMC3557299
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054932
MicroRNA-195 inhibits the proliferation of human glioma cells by directly targeting cyclin D1 and cyclin E1
Abstract
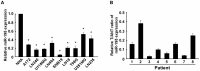
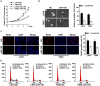
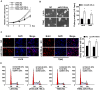
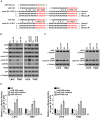
Glioma proliferation is a multistep process during which a sequence of genetic and epigenetic alterations randomly occur to affect the genes controlling cell proliferation, cell death and genetic stability. microRNAs are emerging as important epigenetic modulators of multiple target genes, leading to abnormal cellular signaling involving cellular proliferation in cancers.In the present study, we found that expression of miR-195 was markedly downregulated in glioma cell lines and human primary glioma tissues, compared to normal human astrocytes and matched non-tumor associated tissues. Upregulation of miR-195 dramatically reduced the proliferation of glioma cells. Flow cytometry analysis showed that ectopic expression of miR-195 significantly decreased the percentage of S phase cells and increased the percentage of G1/G0 phase cells. Overexpression of miR-195 dramatically reduced the anchorage-independent growth ability of glioma cells. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-195 downregulated the levels of phosphorylated retinoblastoma (pRb) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in glioma cells. Conversely, inhibition of miR-195 promoted cell proliferation, increased the percentage of S phase cells, reduced the percentage of G1/G0 phase cells, enhanced anchorage-independent growth ability, upregulated the phosphorylation of pRb and PCNA in glioma cells. Moreover, we show that miR-195 inhibited glioma cell proliferation by downregulating expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E1, via directly targeting the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of cyclin D1 and cyclin E1 mRNA. Taken together, our results suggest that miR-195 plays an important role to inhibit the proliferation of glioma cells, and present a novel mechanism for direct miRNA-mediated suppression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E1 in glioma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
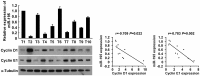
References
-
- Oliver Gautschi, Daniel Ratschiller, Mathias Gugger (2007) Cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung cancer: A key driver of malignant transformation. Lung Cancer 55: 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Lew DJ, Dulić V, Reed SI (1991) Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell 66: 1197–1206. - PubMed
-
- Matsushime H, Roussel MF, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ (1991) Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell 65: 701–713. - PubMed
-
- Motokura T, Bloom T, Kim HG, Jüppner H, Ruderman JV, et al. (1991) A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature 350: 512–515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

