Pencilbeam irradiation technique for whole brain radiotherapy: technical and biological challenges in a small animal model
- PMID: 23383014
- PMCID: PMC3557252
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054960
Pencilbeam irradiation technique for whole brain radiotherapy: technical and biological challenges in a small animal model
Abstract
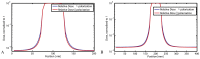
We have conducted the first in-vivo experiments in pencilbeam irradiation, a new synchrotron radiation technique based on the principle of microbeam irradiation, a concept of spatially fractionated high-dose irradiation. In an animal model of adult C57 BL/6J mice we have determined technical and physiological limitations with the present technical setup of the technique. Fifty-eight animals were distributed in eleven experimental groups, ten groups receiving whole brain radiotherapy with arrays of 50 µm wide beams. We have tested peak doses ranging between 172 Gy and 2,298 Gy at 3 mm depth. Animals in five groups received whole brain radiotherapy with a center-to-center (ctc) distance of 200 µm and a peak-to-valley ratio (PVDR) of ∼ 100, in the other five groups the ctc was 400 µm (PVDR ∼ 400). Motor and memory abilities were assessed during a six months observation period following irradiation. The lower dose limit, determined by the technical equipment, was at 172 Gy. The LD50 was about 1,164 Gy for a ctc of 200 µm and higher than 2,298 Gy for a ctc of 400 µm. Age-dependent loss in motor and memory performance was seen in all groups. Better overall performance (close to that of healthy controls) was seen in the groups irradiated with a ctc of 400 µm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





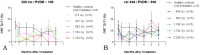


Similar articles
-
Neurologic Changes Induced by Whole-Brain Synchrotron Microbeam Irradiation: 10-Month Behavioral and Veterinary Follow-Up.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 Sep 1;120(1):178-188. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.02.053. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 38462014
-
Effects of pulsed, spatially fractionated, microscopic synchrotron X-ray beams on normal and tumoral brain tissue.Mutat Res. 2010 Apr-Jun;704(1-3):160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20034592 Review.
-
Synchrotron microbeam radiation therapy for rat brain tumor palliation-influence of the microbeam width at constant valley dose.Phys Med Biol. 2009 Nov 7;54(21):6711-24. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/21/017. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Phys Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19841517
-
Response of avian embryonic brain to spatially segmented x-ray microbeams.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2001 May;47(3):485-93. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2001. PMID: 11441956
-
Synchrotron-generated microbeam radiosurgery: a novel experimental approach to modulate brain function.Neurol Res. 2011 Oct;33(8):825-31. doi: 10.1179/016164111X13123658647445. Neurol Res. 2011. PMID: 22004705 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbeam Irradiation as a Simultaneously Integrated Boost in a Conventional Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Protocol.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8319. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158319. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955454 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative toxicity of synchrotron and conventional radiation therapy based on total and partial body irradiation in a murine model.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 13;8(1):12044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30543-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30104646 Free PMC article.
-
Good Timing Matters: The Spatially Fractionated High Dose Rate Boost Should Come First.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 2;14(23):5964. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235964. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497446 Free PMC article.
-
Microbeam radiation therapy - grid therapy and beyond: a clinical perspective.Br J Radiol. 2017 Oct;90(1078):20170073. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170073. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Br J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28749174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid dose calculation: a dose calculation algorithm for microbeam radiation therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2018 Feb 13;63(4):045013. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aaa705. Phys Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29324439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bräuer-Krisch E, Requardt H, Brochard T, Berruyer G, Renier M, et al. (2009) New technology enables high precision multislit collimators for microbeam radiation therapy, Rev Sci Instr. 80: 074301. - PubMed
-
- Laissue JA, Geiser G, Spanne PO, Dilmanian FA, Gebbers JO (1998) Neuropoathology of ablation of rat gliosarcomas and contiguous brain tissues using a microplanar beam of synchrotron-wiggler-generated x-rays. Int J Cancer 78: 654–660. - PubMed
-
- Schültke E, Juurlink B, Ataelmannan K, Laissue J, Blattmann H, et al. (2008) Memory and Survival after Microbeam Radiation Therapy. Eur J Radiol 68S: S142–S146. - PubMed
-
- Laissue JA, Blattmann H, Di Michiel M, Slatkin DN, Lyubimov N, et al. (2001) Weanling piglet cerebellum: a surrogate for tolerance to MRT (microbeam radiation therapy) in pediatric neuro-oncology. Proc SPIE 4508: 65–73.
-
- Bouchet A, Lemasson B, Le Duc G, Maisin C, Bräuer-Krisch E, et al. (2010) Preferential effect of synchrotron microbeam radiation therapy on intracerebral 9L gliosarcoma vascular networks. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(5): 1503–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

