Inhibitors of the influenza A virus M2 proton channel discovered using a high-throughput yeast growth restoration assay
- PMID: 23383318
- PMCID: PMC3562233
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055271
Inhibitors of the influenza A virus M2 proton channel discovered using a high-throughput yeast growth restoration assay
Abstract
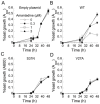
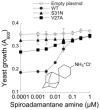
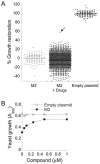
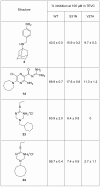
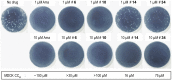
The M2 proton channel of the influenza A virus is the target of the anti-influenza drugs amantadine and rimantadine. The effectiveness of these drugs has been dramatically limited by the rapid spread of drug resistant mutations, mainly at sites S31N, V27A and L26F in the pore of the channel. Despite progress in designing inhibitors of V27A and L26F M2, there are currently no drugs targeting these mutated channels in clinical trials. Progress in developing new drugs has been hampered by the lack of a robust assay with sufficient throughput for discovery of new active chemotypes among chemical libraries and sufficient sensitivity to provide the SAR data essential for their improvement and development as drugs. In this study we adapted a yeast growth restoration assay, in which expression of the M2 channel inhibits yeast growth and exposure to an M2 channel inhibitor restores growth, into a robust and sensitive high-throughput screen for M2 channel inhibitors. A screen of over 250,000 pure chemicals and semi-purified fractions from natural extracts identified 21 active compounds comprising amantadine, rimantadine, 13 related adamantanes and 6 non-adamantanes. Of the non-adamantanes, hexamethylene amiloride and a triazine derivative represented new M2 inhibitory chemotypes that also showed antiviral activity in a plaque reduction assay. Of particular interest is the fact that the triazine derivative was not sufficiently potent for detection as an inhibitor in the traditional two electrode voltage clamp assay for M2 channel activity, but its discovery in the yeast assay led to testing of analogues of which one was as potent as amantadine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Influenza (Seasonal). Fact sheet No. 211, Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/index.html. Accessed 2012 August 2.
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 75, Available: http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_11_20a/en/index.html.Accessed 2012 August 2.
-
- Viboud C, Simonsen L (2012) Global mortality of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1. The Lancet Infectious Diseases doi:10.1016/S1473–3099(12)70152–4. - PubMed
-
- Das K (2012) Antivirals Targeting Influenza A Virus. J Med Chem ASAP. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

