Hepatitis B reactivation related to everolimus
- PMID: 23383366
- PMCID: PMC3562726
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i1.43
Hepatitis B reactivation related to everolimus
Abstract
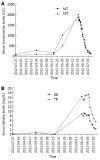
Reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) during chemotherapy is a well known complication in patients with chronic hepatitis B and cancer. The clinical manifestations range from subclinical elevation of liver enzymes to severe, potentially fatal fulminant hepatitis. Reactivation can occur in a patient with previous inactive HBV infection; either an inactive carrier or a patient with resolved hepatitis. Everolimus is a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor approved in renal cell carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumours and breast cancer. mTOR inhibitors are a new generation of drugs for targeted treatment; therefore, little about their side effects is known. Here, we report a patient with renal cell carcinoma who experienced a flare of hepatitis B infection during treatment with everolimus. Clinicians should be aware of HBV reactivation in patients who are undergoing treatment with everolimus, and screening for hepatitis B infection and prophylactic antiviral treatment should be considered.
Keywords: Everolimus; Hepatitis B; Immunosuppressive treatment; Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors; Renal cell carcinoma; Virus reactivation.
Figures
References
-
- Oketani M, Ido A, Uto H, Tsubouchi H. Prevention of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy or chemotherapy. Hepatol Res. 2012;42:627–636. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, et al. Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma : final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 2010;116:4256–4265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous