Tau is reduced in AD plasma and validation of employed ELISA methods
- PMID: 23383382
- PMCID: PMC3560452
Tau is reduced in AD plasma and validation of employed ELISA methods
Abstract
Objective: Measure total tau levels in the circulation of living humans, validate the methods employed and determine if there are consistent differences in total tau levels between normal controls and individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and/or Alzheimer's disease (AD).
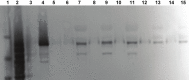
Methods: Employing ELISA methods, validated by Western bolts using three separate tau antibodies, we quantified total tau levels in serially collected serum and plasma samples from individuals longitudinally evaluated for cognitive performance.
Results: We identified substantial levels of tau in human circulation using plasma, but not serum. The measurement of authentic tau protein was verified by Western blots using a C-terminal specific antibody, an N-terminal specific antibody and antibody used in the commercially available ELISA kit. We revealed a significant decrease in plasma levels of total tau among subjects with MCI compared to cognitively normal controls, with a further highly significant reduction in AD patients compared to both MCI and normal controls. We also found a significant positive correlation between changing levels of plasma tau and cognitive performance within the entire population and among AD patients.
Conclusions: The data suggest that changes in circulating tau levels quantified in plasma samples, but not serum samples, may represent a viable biomarker for tracking the progression of AD and the efficacy of medications in its treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Circulating tau levels; mild cognitive impairment.
Figures

References
-
- Ewers M, Buerger K, Teipel SJ, Scheltens P, Schroder J, Zinkowski RP, Bouwman FH, Schonknecht P, Schoonenboom NS, Andreasen N, Wallin AK, DeBernardis JF, Kerkman DJ, Heindl B, Blennow K, Hampel H. Multicenter assessment of CSF-phosphorylated tau for the prediction of conversion of MCI. Neurology. 2007;69:2205–2212. - PubMed
-
- Olsson A, Vanderstichele H, Andreasen N, De Meyer G, Wallin A, Holmberg B, Rosengren L, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K. Simultaneous measurement of beta-amyloid (1-42), total tau and phosphorylated tau (Thr81) in cerebrospinal fluid by the xMAP technology. Clin Chem. 2005;51:336–345. - PubMed
-
- Vanderstichele H, De Meyer G, Shapiro F, Engelborghs S, De Deyn PP, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ. Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers: From concept to clinical utility. In: Galimberti D, Scarpini E, editors. Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease. Nova Science Publishers; 2008. pp. 81–122.
-
- de Leon MJ, Mosconi L, Blennow K, DeSanti S, Zinkowski RP, Mehta PD, Pratico D, Tsui W, Saint Louis LA, Sobanska L, Brys M, Li Y, Rich K, Rinne J, Rusinek H. Imaging and CSF studies in the preclinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1097:114–145. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
