High level expression and facile purification of recombinant silk-elastin-like polymers in auto induction shake flask cultures
- PMID: 23384239
- PMCID: PMC3599559
- DOI: 10.1186/2191-0855-3-11
High level expression and facile purification of recombinant silk-elastin-like polymers in auto induction shake flask cultures
Abstract
Silk-elastin-like polymers (SELPs) are protein-based polymers composed of repetitive amino acid sequence motifs found in silk fibroin (GAGAGS) and mammalian elastin (VPGVG). These polymers are of much interest, both from a fundamental and applied point of view, finding potential application in biomedicine, nanotechnology and as materials. The successful employment of such polymers in such diverse fields, however, requires the ready availability of a variety of different forms with novel enhanced properties and which can be simply prepared in large quantities on an industrial scale. In an attempt to create new polymer designs with improved properties and applicability, we have developed four novel SELPs wherein the elastomer forming sequence poly(VPGVG) is replaced with a plastic-like forming sequence, poly(VPAVG), and combined in varying proportions with the silk motif. Furthermore, we optimised a simplified production procedure for these, making use of an autoinduction medium to reduce process intervention and with the production level obtained being 6-fold higher than previously reported for other SELPs, with volumetric productivities above 150 mg/L. Finally, we took advantage of the known enhanced stability of these polymers in developing an abridged, non-chromatographic downstream processing and purification protocol. A simple acid treatment allowed for cell disruption and the obtention of relative pure SELP in one-step, with ammonium sulphate precipitation being subsequently used to enable improved purity. These simplified production and purification procedures improve process efficiency and reduce costs in the preparation of these novel polymers and enhances their potential for application.
Figures

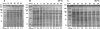
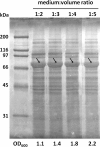
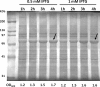
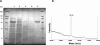




References
-
- Cappello J, Crissman JW, Crissman M, Ferrari FA, Textor G, Wallis O, Whitledge JR, Zhou X, Burman D, Aukerman L, Stedronsky ER. In-situ self-assembling protein polymer gel systems for administration, delivery, and release of drugs. J Control Release. 1998;3(1–3):105–117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

