Visual assessment of brain magnetic resonance imaging detects injury to cognitive regulatory sites in patients with heart failure
- PMID: 23384634
- PMCID: PMC4249656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2012.12.001
Visual assessment of brain magnetic resonance imaging detects injury to cognitive regulatory sites in patients with heart failure
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) patients exhibit depression and executive function impairments that contribute to HF mortality. Using specialized magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) analysis procedures, brain changes appear in areas regulating these functions (mammillary bodies, hippocampi, and frontal cortex). However, specialized MRI procedures are not part of standard clinical assessment for HF (which is usually a visual evaluation), and it is unclear whether visual MRI examination can detect changes in these structures.
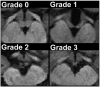
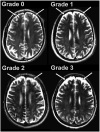
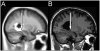
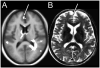
Methods and results: Using brain MRI, we visually examined the mammillary bodies and frontal cortex for global and hippocampi for global and regional tissue changes in 17 HF and 50 control subjects. Significantly global changes emerged in the right mammillary body (HF 1.18 ± 1.13 vs control 0.52 ± 0.74; P = .024), right hippocampus (HF 1.53 ± 0.94 vs control 0.80 ± 0.86; P = .005), and left frontal cortex (HF 1.76 ± 1.03 vs control 1.24 ± 0.77; P = .034). Comparison of the visual method with specialized MRI techniques corroborates right hippocampal and left frontal cortical, but not mammillary body, tissue changes.
Conclusions: Visual examination of brain MRI can detect damage in HF in areas regulating depression and executive function, including the right hippocampus and left frontal cortex. Visual MRI assessment in HF may facilitate evaluation of injury to these structures and the assessment of the impact of potential treatments for this damage.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Heart failure--an identified but largely ignored source of errors in postmortem brain volume studies.J Card Fail. 2013 Aug;19(8):600. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2013.05.013. J Card Fail. 2013. PMID: 23910591 No abstract available.
-
Heart failure-a common disease, but not an "error".J Card Fail. 2013 Aug;19(8):601-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2013.06.299. J Card Fail. 2013. PMID: 23910592 No abstract available.
References
-
- Desmond PM, O'Brien JT, Tress BM, Ames DJ, Clement JG, Clement P, et al. Volumetric and visual assessment of the mesial temporal structures in Alzheimer's disease. Aust N Z J Med. 1994;24:547–53. - PubMed
-
- de Leon MJ, George AE, Reisberg B, Ferris SH, Kluger A, Stylopoulos LA, et al. Alzheimer's disease: longitudinal CT studies of ventricular change. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989;152:1257–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

