Identification of quercitrin as an inhibitor of the p90 S6 ribosomal kinase (RSK): structure of its complex with the N-terminal domain of RSK2 at 1.8 Å resolution
- PMID: 23385462
- PMCID: PMC3565440
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444912045520
Identification of quercitrin as an inhibitor of the p90 S6 ribosomal kinase (RSK): structure of its complex with the N-terminal domain of RSK2 at 1.8 Å resolution
Abstract
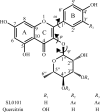
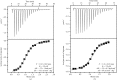
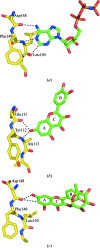
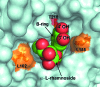
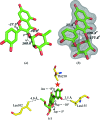
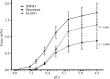
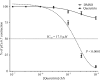
Members of the RSK family of kinases constitute attractive targets for drug design, but a lack of structural information regarding the mechanism of selective inhibitors impedes progress in this field. The crystal structure of the N-terminal kinase domain (residues 45-346) of mouse RSK2, or RSK2(NTKD), has recently been described in complex with one of only two known selective inhibitors, a rare naturally occurring flavonol glycoside, kaempferol 3-O-(3'',4''-di-O-acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranoside), known as SL0101. Based on this structure, it was hypothesized that quercitrin (quercetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside), a related but ubiquitous and inexpensive compound, might also act as an RSK inhibitor. Here, it is demonstrated that quercitrin binds to RSK2(NTKD) with a dissociation constant (K(d)) of 5.8 µM as determined by isothermal titration calorimetry, and a crystal structure of the binary complex at 1.8 Å resolution is reported. The crystal structure reveals a very similar mode of binding to that recently reported for SL0101. Closer inspection shows a number of small but significant differences that explain the slightly higher K(d) for quercitrin compared with SL0101. It is also shown that quercitrin can effectively substitute for SL0101 in a biological assay, in which it significantly suppresses the contractile force in rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle in response to Ca(2+).
Keywords: SL0101; flavonol glycosides; inhibitors; protein kinases; quercitrin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insights into the inhibition of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) by the flavonol glycoside SL0101 from the 1.5 Å crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of RSK2 with bound inhibitor.Biochemistry. 2012 Aug 21;51(33):6499-510. doi: 10.1021/bi300620c. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22846040 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying requirements for RSK2 specific inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):1798-1809. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1957862. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34348556 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of rhamnose substituents on the potency of SL0101, an inhibitor of the Ser/Thr kinase, RSK.Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Sep 1;14(17):6034-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.05.009. Epub 2006 May 24. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16723233
-
The unusual mechanism of inhibition of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) by flavonol rhamnosides.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1834(7):1285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.03.018. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23541530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting RSK2 in Cancer Therapy: A Review of Natural Products.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(1):35-41. doi: 10.2174/0118715206329546240830055233. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39248063 Review.
Cited by
-
Disordered Protein Kinase Regions in Regulation of Kinase Domain Cores.Trends Biochem Sci. 2019 Apr;44(4):300-311. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.12.002. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019. PMID: 30611608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Assessment of Dispersion-Corrected DFT Methods for Modeling Nonbonded Interactions in Protein Kinase Inhibitor Complexes.Molecules. 2024 Jan 6;29(2):0. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020304. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257217 Free PMC article.
-
RSK1 vs. RSK2 Inhibitory Activity of the Marine β-Carboline Alkaloid Manzamine A: A Biochemical, Cervical Cancer Protein Expression, and Computational Study.Mar Drugs. 2021 Sep 7;19(9):506. doi: 10.3390/md19090506. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34564169 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and Biochemical Discovery of RSK2 as a Novel Target for Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG).PLoS One. 2015 Jun 17;10(6):e0130049. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130049. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26083344 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Conformational Analyses of Naturally Occurring Flavonoid-O-Glycosides with Unnatural Flavonoid-CF2-Glycosides Using Molecular Modeling.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Jan 9;63(1):375-386. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01147. Epub 2022 Dec 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 36512328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221.
-
- Anjum, R. & Blenis, J. (2008). Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 747–758. - PubMed
-
- Boly, R., Gras, T., Lamkami, T., Guissou, P., Serteyn, D., Kiss, R. & Dubois, J. (2011). Int. J. Oncol. 38, 833–842. - PubMed
-
- Calderón-Montaño, J. M., Burgos-Morón, E., Pérez-Guerrero, C. & López-Lázaro, M. (2011). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 11, 298–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

