Immune cell infiltration as an indicator of the immune microenvironment of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 23385730
- PMCID: PMC3590668
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.32
Immune cell infiltration as an indicator of the immune microenvironment of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: The host immune reaction is represented by immune/inflammatory cell infiltrates. Here we systematically analysed tumour-infiltrating immune/inflammatory cells in pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDC) and evaluated their clinicopathological impact.
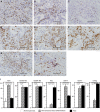
Methods: Using immunohistochemistry, we examined tumour-infiltrating CD68(+) pan-macrophages, HLA-DR(+)CD68(+) M1 macrophages (M1), CD163(+) or CD204(+) M2 macrophages (M2), CD66b(+) neutrophils (Neu), CD4(+) T cells (CD4(+)T), CD8(+) T cells (CD8(+)T), and FOXP3(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells (Treg) in 212 cases of PDC, and conducted correlation and survival analyses using the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards model.
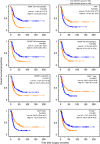
Results: Higher levels of tumour-infiltrating pan-macrophages, M2, Neu, or the ratio of Tregs to CD4(+)T (%Treg) were significantly associated with shorter survival, whereas higher levels of tumour-infiltrating CD4(+)T, CD8(+)T, or the ratio of M1 to pan-macrophages (%M1) were significantly associated with longer survival. Survival analysis of pairs of these variables revealed that some of the resulting patient groups had exclusively longer survival. We then connected the apparently related factors, and two significant variables emerged: tumour-infiltrating CD4(+)T(high)/CD8(+)T(high)/%Treg(low) and tumour-infiltrating %M1(high)/M2(low). Multivariate survival analysis revealed that these variables were significantly correlated with longer survival and had a higher hazard ratio.
Conclusion: Tumour-infiltrating CD4(+)T(high)/CD8(+)T(high)/%Treg(low) and %M1(high)/M2(low) are independent prognosticators useful for evaluating the immune microenvironment of PDC.
Figures

References
-
- Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Caruso RA, Bellocco R, Pagano M, Bertoli G, Rigoli L, Inferrera C. Prognostic value of intratumoral neutrophils in advanced gastric carcinoma in a high-risk area in northern Italy. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:831–837. - PubMed
-
- Center for Cancer Control and Information Services, National Cancer Center . Cancer Statistics in Japan. Center for Cancer Control and Information Services, National Cancer Center, Tokyo, Japan; 2009.
-
- Corzo CA, Condamine T, Lu L, Cotter MJ, Youn JI, Cheng P, Cho HI, Celis E, Quiceno DG, Padhya T, McCaffrey TV, McCaffrey JC, Gabrilovich DI. HIF-1alpha regulates function and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. J Exp Med. 2010;207:2439–2453. - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Monte L, Reni M, Tassi E, Clavenna D, Papa I, Recalde H, Braga M, Di Carlo V, Doglioni C, Protti MP. Intratumor T helper type 2 cell infiltrate correlates with cancer-associated fibroblast thymic stromal lymphopoietin production and reduced survival in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med. 2011;208:469–478. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

