Facility optimization to improve activation rate distributions during IVNAA
- PMID: 23386375
- PMCID: PMC3650749
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrs124
Facility optimization to improve activation rate distributions during IVNAA
Abstract
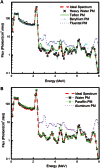
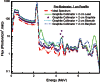
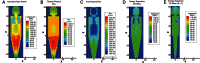
Currently, determination of body composition is the most useful method for distinguishing between certain diseases. The prompt-gamma in vivo neutron activation analysis (IVNAA) facility for non-destructive elemental analysis of the human body is the gold standard method for this type of analysis. In order to obtain accurate measurements using the IVNAA system, the activation probability in the body must be uniform. This can be difficult to achieve, as body shape and body composition affect the rate of activation. The aim of this study was to determine the optimum pre-moderator, in terms of material for attaining uniform activation probability with a CV value of about 10% and changing the collimator role to increase activation rate within the body. Such uniformity was obtained with a high thickness of paraffin pre-moderator, however, because of increasing secondary photon flux received by the detectors it was not an appropriate choice. Our final calculations indicated that using two paraffin slabs with a thickness of 3 cm as a pre-moderator, in the presence of 2 cm Bi on the collimator, achieves a satisfactory distribution of activation rate in the body.
Keywords: IVNAA; MCNP; activation rate; collimator; neutron flux uniformity; pre-moderator.
Figures





References
-
- Kenneth JE. In vivo neutron activation analysis. In: Aflassi ZB, editor. Activation Analysis. 2nd vol. Boka Raton, Florida: CRC Press; 1990. pp. 407–24.
-
- Anderson J, Osborn SB, Tomlinson RWS, et al. Neutron activation analysis in man in vivo: a new technique in medical investigation. Lancet. 1964;2:1201–5. - PubMed
-
- Chettle DR, Fremlin JH. Techniques of in vivo neutron activation analysis. Phys Med Biol. 1984;29:1011–43. - PubMed
-
- Miri Hakimabad H, Rafat Motavalli L. Improving the uniformity of the gamma production rate distribution with depth in a large biological sample for an IVNAA facility. J Nucl Technol Radiat. 2009;24:119–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

