Toll-like receptor 2 mediates peripheral nerve injury-induced NADPH oxidase 2 expression in spinal cord microglia
- PMID: 23386616
- PMCID: PMC3597798
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.414904
Toll-like receptor 2 mediates peripheral nerve injury-induced NADPH oxidase 2 expression in spinal cord microglia
Abstract
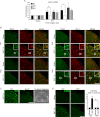
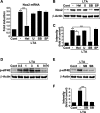
We have previously reported that NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2) is up-regulated in spinal cord microglia after spinal nerve injury, demonstrating that it is critical for microglia activation and subsequent pain hypersensitivity. However, the mechanisms and molecules involved in Nox2 induction have not been elucidated. Previous studies have shown that Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are involved in nerve injury-induced spinal cord microglia activation. In this study, we investigated the role of TLR in Nox2 expression in spinal cord microglia after peripheral nerve injury. Studies using TLR knock-out mice have shown that nerve injury-induced microglial Nox2 up-regulation is abrogated in TLR2 but not in TLR3 or -4 knock-out mice. Intrathecal injection of lipoteichoic acid, a TLR2 agonist, induced Nox2 expression in spinal cord microglia both at the mRNA and protein levels. Similarly, lipoteichoic acid stimulation induced Nox2 expression and reactive oxygen species production in primary spinal cord glial cells in vitro. Studies on intracellular signaling pathways indicate that NF-κB and p38 MAP kinase activation is required for TLR2-induced Nox2 expression in glial cells. Conclusively, our data show that TLR2 mediates nerve injury-induced Nox2 gene expression in spinal cord microglia via NF-κB and p38 activation and thereby may contribute to spinal cord microglia activation.
Figures




References
-
- Watkins L. R., Maier S. F. (2003) Glia: a novel drug discovery target for clinical pain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 973–985 - PubMed
-
- Milligan E. D., Mehmert K. K., Hinde J. L., Harvey L. O., Martin D., Tracey K. J., Maier S. F., Watkins L. R. (2000) Thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia produced by intrathecal administration of the human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein, gp120. Brain Res. 861, 105–116 - PubMed
-
- Raghavendra V., Tanga F., DeLeo J. A. (2003) Inhibition of microglial activation attenuates the development but not existing hypersensitivity in a rat model of neuropathy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 306, 624–630 - PubMed
-
- Coull J. A., Beggs S., Boudreau D., Boivin D., Tsuda M., Inoue K., Gravel C., Salter M. W., De Koninck Y. (2005) BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 438, 1017–1021 - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki Y., Zhang L., Cheng J. K., Ji R. R. (2008) Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 28, 5189–5194 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

