Genetic associations with valvular calcification and aortic stenosis
- PMID: 23388002
- PMCID: PMC3766627
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1109034
Genetic associations with valvular calcification and aortic stenosis
Abstract
Background: Limited information is available regarding genetic contributions to valvular calcification, which is an important precursor of clinical valve disease.
Methods: We determined genomewide associations with the presence of aortic-valve calcification (among 6942 participants) and mitral annular calcification (among 3795 participants), as detected by computed tomographic (CT) scanning; the study population for this analysis included persons of white European ancestry from three cohorts participating in the Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology consortium (discovery population). Findings were replicated in independent cohorts of persons with either CT-detected valvular calcification or clinical aortic stenosis.
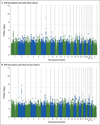
Results: One SNP in the lipoprotein(a) (LPA) locus (rs10455872) reached genomewide significance for the presence of aortic-valve calcification (odds ratio per allele, 2.05; P=9.0×10(-10)), a finding that was replicated in additional white European, African-American, and Hispanic-American cohorts (P<0.05 for all comparisons). Genetically determined Lp(a) levels, as predicted by LPA genotype, were also associated with aortic-valve calcification, supporting a causal role for Lp(a). In prospective analyses, LPA genotype was associated with incident aortic stenosis (hazard ratio per allele, 1.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.32 to 2.15) and aortic-valve replacement (hazard ratio, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.05 to 2.27) in a large Swedish cohort; the association with incident aortic stenosis was also replicated in an independent Danish cohort. Two SNPs (rs17659543 and rs13415097) near the proinflammatory gene IL1F9 achieved genomewide significance for mitral annular calcification (P=1.5×10(-8) and P=1.8×10(-8), respectively), but the findings were not replicated consistently.
Conclusions: Genetic variation in the LPA locus, mediated by Lp(a) levels, is associated with aortic-valve calcification across multiple ethnic groups and with incident clinical aortic stenosis. (Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and others.).
Figures
Comment in
-
Shared genetic risk for sclerosis of valves and vessels.N Engl J Med. 2013 Feb 7;368(6):569-70. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1215152. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23388009 No abstract available.
-
Valvular disease: Lipoprotein(a) link to calcification.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013 Apr;10(4):180. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.24. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23438687 No abstract available.
References
-
- Carabello BA, Paulus WJ. Aortic stenosis. Lancet. 2009;373:956–966. - PubMed
-
- Cosmi JE, Kort S, Tunick PA, et al. The risk of the development of aortic stenosis in patients with “benign” aortic valve thickening. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:2345–2347. - PubMed
-
- Otto CM, Lind BK, Kitzman DW, Gersh BJ, Siscovick DS. Association of aortic-valve sclerosis with cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in the elderly. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:142–147. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Vasan RS, Parise H, et al. Mitral annular calcification predicts cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2003;107:1492–1496. - PubMed
-
- Bella JN, Tang WH, Kraja A, et al. Genome-wide linkage mapping for valve calcification susceptibility loci in hyper- tensive sibships: the Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network Study. Hypertension. 2007;49:453–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HL-071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002317/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02-HL-6-4278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071739/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG012100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071739/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR-024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
