Sulforaphane inhibits growth of phenotypically different breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23389114
- PMCID: PMC3832756
- DOI: 10.1007/s00394-013-0499-5
Sulforaphane inhibits growth of phenotypically different breast cancer cells
Erratum in
- Eur J Nutr. 2013 Dec;52(8):1959
Abstract
Purpose: Cancer development and resistance to chemotherapy correlates with aberrant activity of mitogenic pathways. In breast cancers, pro-survival PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K1 [corrected] signaling pathway is often hyperactive due to overexpression of genes coding for growth factors or estrogen receptors, constitutive activation of PI3K or Akt and loss of PTEN, a negative regulator of the pathway. Since epidemiologic as well as rodent tumor studies indicate that sulforaphane (SFN), a constituent of many edible cruciferous vegetables, might be a potent inhibitor of mammary carcinogenesis, we analyzed the response of four breast cancer cell lines representing different abnormalities in ErbB2/ER-PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K1[corrected] signaling pathway to this compound.
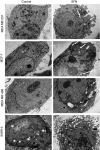
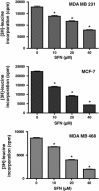
Methods: Four different breast cancer cell lines were used: MDA MB 231, MCF-7, SKBR-3 and MDA MB 468. Cell viability and ultrastructure, protein synthesis, autophagy induction and phosphorylation status of Akt and S6K1 kinases upon SFN treatment were determined.
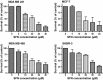
Results: We observed that all four cell lines are similarly sensitive to SFN. SFN decreased phosphorylation of Akt and S6K1 kinases and at higher concentrations induced autophagy in all studied cell lines. Moreover, global protein synthesis was inhibited by SFN in investigated cell lines in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: These results indicate that SFN is a potent inhibitor of the viability of breast cancer cells representing different activity of the ErbB2/ER-PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K1 [corrected] pro-survival pathway and suggest that it targets downstream elements of the pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sensitization of HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Cells to Lapatinib Using Plants-Derived Isothiocyanates.Nutr Cancer. 2015;67(6):976-86. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2015.1053498. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Nutr Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26134366
-
Inhibition of Autophagy Increases Proliferation Inhibition and Apoptosis Induced by the PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in Breast Cancer Cells.Clin Lab. 2015;61(8):1043-51. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2015.150144. Clin Lab. 2015. PMID: 26427150
-
Resveratrol enhances the anti-tumor activity of the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin in multiple breast cancer cell lines mainly by suppressing rapamycin-induced AKT signaling.Cancer Lett. 2011 Feb 28;301(2):168-76. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.11.012. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21168265
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway in breast cancer.Oncologist. 2011;16(4):404-14. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0402. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Oncologist. 2011. PMID: 21406469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Pathways Related to Sulforaphane as Adjuvant Treatment: A Nanomedicine Perspective in Breast Cancer.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Oct 1;58(10):1377. doi: 10.3390/medicina58101377. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36295538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
S-Allyl-L-Cysteine Affects Cell Proliferation and Expression of H2S-Synthetizing Enzymes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 4;14(2):188. doi: 10.3390/biom14020188. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397425 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Phytochemicals in Cancer Chemoprevention: Insights.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 14;10(9):1455. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091455. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR inhibitor PP242 increases antitumor activity of sulforaphane by blocking Akt/mTOR pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):451-461. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06895-9. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34731371
-
Targeting Drug Chemo-Resistance in Cancer Using Natural Products.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 29;9(10):1353. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101353. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isothiocyanates induce autophagy and inhibit protein synthesis in primary cells via modulation of AMPK-mTORC1-S6K1 signaling pathway, and protect against mutant huntingtin aggregation.Eur J Nutr. 2024 Dec 16;64(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03539-z. Eur J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39680190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianco R, Shin I, Ritter CA, Yakes FM, Basso A, Rosen N, Tsurutani J, Dennis PA, Mills GB, Arteaga CL. Loss of PTEN/MMAC1/TEP in EGF receptor-expressing tumor cells counteracts the antitumor action of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 2003;22:2812–2822. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206388. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

