APOBEC3B is an enzymatic source of mutation in breast cancer
- PMID: 23389445
- PMCID: PMC3907282
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11881
APOBEC3B is an enzymatic source of mutation in breast cancer
Erratum in
- Nature. 2013 Oct 24;502(7472):580
Abstract
Several mutations are required for cancer development, and genome sequencing has revealed that many cancers, including breast cancer, have somatic mutation spectra dominated by C-to-T transitions. Most of these mutations occur at hydrolytically disfavoured non-methylated cytosines throughout the genome, and are sometimes clustered. Here we show that the DNA cytosine deaminase APOBEC3B is a probable source of these mutations. APOBEC3B messenger RNA is upregulated in most primary breast tumours and breast cancer cell lines. Tumours that express high levels of APOBEC3B have twice as many mutations as those that express low levels and are more likely to have mutations in TP53. Endogenous APOBEC3B protein is predominantly nuclear and the only detectable source of DNA C-to-U editing activity in breast cancer cell-line extracts. Knockdown experiments show that endogenous APOBEC3B correlates with increased levels of genomic uracil, increased mutation frequencies, and C-to-T transitions. Furthermore, induced APOBEC3B overexpression causes cell cycle deviations, cell death, DNA fragmentation, γ-H2AX accumulation and C-to-T mutations. Our data suggest a model in which APOBEC3B-catalysed deamination provides a chronic source of DNA damage in breast cancers that could select TP53 inactivation and explain how some tumours evolve rapidly and manifest heterogeneity.
Figures
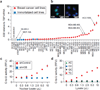
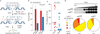
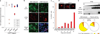

Comment in
-
Genomic instability: DNA transitions.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Apr;13(4):220-1. doi: 10.1038/nrc3490. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23486239 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sjöblom T, et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2006;314:268–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI083196/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA077598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA033186/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- T32 CA009138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000114/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA101955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1RR033183/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA77598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033183/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM091743/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR033182/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM095219/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI064046/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

