Evidence for dynein and astral microtubule-mediated cortical release and transport of Gαi/LGN/NuMA complex in mitotic cells
- PMID: 23389635
- PMCID: PMC3608500
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-06-0458
Evidence for dynein and astral microtubule-mediated cortical release and transport of Gαi/LGN/NuMA complex in mitotic cells
Abstract
Spindle positioning is believed to be governed by the interaction between astral microtubules and the cell cortex and involve cortically anchored motor protein dynein. How dynein is recruited to and regulated at the cell cortex to generate forces on astral microtubules is not clear. Here we show that mammalian homologue of Drosophila Pins (Partner of Inscuteable) (LGN), a Gαi-binding protein that is critical for spindle positioning in different systems, associates with cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain (DYNC1H1) in a Gαi-regulated manner. LGN is required for the mitotic cortical localization of DYNC1H1, which, in turn, also modulates the cortical accumulation of LGN. Using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching analysis, we show that cortical LGN is dynamic and the turnover of LGN relies, at least partially, on astral microtubules and DYNC1H1. We provide evidence for dynein- and astral microtubule-mediated transport of Gαi/LGN/nuclear mitotic apparatus (NuMA) complex from cell cortex to spindle poles and show that actin filaments counteract such transport by maintaining Gαi/LGN/NuMA and dynein at the cell cortex. Our results indicate that astral microtubules are required for establishing bipolar, symmetrical cortical LGN distribution during metaphase. We propose that regulated cortical release and transport of LGN complex along astral microtubules may contribute to spindle positioning in mammalian cells.
Figures
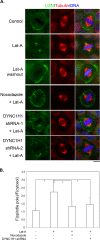
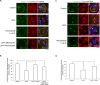
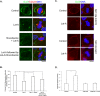
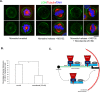
Similar articles
-
RanGTP and CLASP1 cooperate to position the mitotic spindle.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Aug;24(16):2506-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-03-0150. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23783028 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome- and spindle-pole-derived signals generate an intrinsic code for spindle position and orientation.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Feb 12;14(3):311-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb2440. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22327364 Free PMC article.
-
Ric-8A and Gi alpha recruit LGN, NuMA, and dynein to the cell cortex to help orient the mitotic spindle.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(14):3519-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00394-10. Epub 2010 May 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20479129 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mitotic spindle orientation: an integrated view.EMBO Rep. 2016 Aug;17(8):1106-30. doi: 10.15252/embr.201642292. Epub 2016 Jul 18. EMBO Rep. 2016. PMID: 27432284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the inscrutable role of Inscuteable: structural basis and functional implications for the competitive binding of NuMA and Inscuteable to LGN.Open Biol. 2012 Aug;2(8):120102. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120102. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22977735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RanGTP and CLASP1 cooperate to position the mitotic spindle.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Aug;24(16):2506-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-03-0150. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23783028 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylated importin α regulates mitotic spindle orientation through interaction with NuMA.EMBO Rep. 2025 Jul;26(13):3280-3304. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00484-8. Epub 2025 May 27. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425783 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Mitotic Apparatus (NuMA) Interacts with and Regulates Astrin at the Mitotic Spindle.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 16;291(38):20055-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.724831. Epub 2016 Jul 26. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27462074 Free PMC article.
-
Eph signaling controls mitotic spindle orientation and cell proliferation in neuroepithelial cells.J Cell Biol. 2019 Apr 1;218(4):1200-1217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201807157. Epub 2019 Feb 26. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30808706 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-regulated membrane binding of NuMA contributes to efficient anaphase chromosome separation.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Mar;25(5):606-19. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-08-0474. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24371089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahringer J. Control of cell polarity and mitotic spindle positioning in animal cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yair R, Kahane N, Kalcheim C. LGN-dependent orientation of cell divisions in the dermomyotome controls lineage segregation into muscle and dermis. Development. 2011;138:4155–4166. - PubMed
-
- Bowman SK, Neumuller RA, Novatchkova M, Du Q, Knoblich JA. The Drosophila NuMA homolog Mud regulates spindle orientation in asymmetric cell division. Dev Cell. 2006;10:731–742. - PubMed
-
- Busson S, Dujardin D, Moreau A, Dompierre J, De Mey JR. Dynein and dynactin are localized to astral microtubules and at cortical sites in mitotic epithelial cells. Curr Biol. 1998;8:541–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

