Postdural puncture headache in migraineurs and nonheadache subjects: a prospective study
- PMID: 23390176
- PMCID: PMC3653212
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182840bf6
Postdural puncture headache in migraineurs and nonheadache subjects: a prospective study
Abstract
Objectives: To prospectively assess 1) the incidence and duration of postdural puncture headache (PDPH) in migraineurs and healthy subjects; 2) the associated risk factors; and 3) the risk of getting a migraine attack shortly before or after lumbar puncture (LP).
Methods: As part of an extensive biochemical migraine research program, we assessed the occurrence, duration, and characteristics of PDPH in 160 migraineurs and 53 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. In addition, we evaluated potential risk factors for PDPH as well as the risk of developing a migraine attack before or after LP.
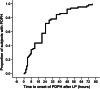
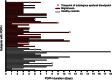
Results: In total, 64 of 199 subjects (32.2%) developed PDPH. Young age, low body mass index, severe headache immediately after LP, and sitting sampling position, but not being a migraineur, increased the risk of PDPH (all p < 0.05). Duration of PDPH was prolonged by history of depression, sitting sampling position, high perceived stress during the LP procedure, and multiple LP efforts (all p < 0.05). Migraine attacks were less likely to occur before or shortly after LP.
Conclusions: Migraineurs are not at increased risk of developing PDPH. PDPH duration is similar in migraineurs and age- and sex-matched controls. LP does not trigger migraine attacks, and the stress of an upcoming LP might even have a protective effect against onset of migraine attacks.
Figures
References
-
- Evans RW, Armon C, Frohman EM, Goodin DS. Assessment: prevention of post-lumbar puncture headaches: report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2000;55:909–914 - PubMed
-
- Olsen KS. Epidural blood patch in the treatment of post-lumbar puncture headache. Pain 1987;30:293–301 - PubMed
-
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;1:9–160 - PubMed
-
- Weeks SK. Spinal headache—prevention and treatment. Can J Anaesth 1990;37:Sliii–Slxiii - PubMed
-
- Fog J, Wang LP, Sundberg A, Mucchiano C. Hearing loss after spinal anesthesia is related to needle size. Anesth Analg 1990;70:517–522 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
