An epidemiologic update on hepatitis C infection in persons living with or at risk of HIV infection
- PMID: 23390299
- PMCID: PMC3565593
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis927
An epidemiologic update on hepatitis C infection in persons living with or at risk of HIV infection
Abstract
Due to shared routes of transmission, coinfection with both human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) is relatively common and results in accelerated liver disease, driving morbidity and mortality. Deaths related to HCV now exceed deaths related to HIV in the United States, and co-infected patients bear a significant proportion of that mortality. This burden may be addressed by novel antiviral therapies that promise increased rates of cure or by enhanced access to liver transplantation, but these are costly interventions. Ultimately, the future burden of coinfection is addressed by greater understanding of who is at risk for development of each infection, thus guiding preventive efforts. Key recent reports regarding the US burden of morbidity and mortality due to HCV and groups at risk for coinfection are reviewed, with a focus on recently described HCV occurring among young injection drug users and men who have sex with men. Given the lack of available vaccine against HCV, enhanced detection and surveillance is a vital component of our public health strategy to combat HCV.
Figures
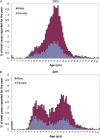
References
-
- Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:705–14. - PubMed
-
- Ly KN, Xing J, Klevens RM, Jiles RB, Ward JW, Holmberg SD. The increasing burden of mortality from viral hepatitis in the United States between 1999 and 2007. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156:271–8. - PubMed
-
- Weber R, Sabin CA, Friis-Moller N, et al. Liver-related deaths in persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus: the D:A:D study. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1632–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

