A single dose of amoxicillin and dexamethasone for prevention of postoperative complications in third molar surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 23390473
- PMCID: PMC3564565
- DOI: 10.4021/jocmr1160w
A single dose of amoxicillin and dexamethasone for prevention of postoperative complications in third molar surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of a single prophylactic dose of amoxicillin and/or dexamethasone in preventing postoperative complications (PC) after a surgical removal of a single mandibular third molar (M3).
Methods: This study is a randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial. Four groups were included: Group 1 (G1) included a prophylactic dose of 2 g of amoxicillin and 8 mg of dexamethasone; Group 2 (G2) included a prophylactic dose of 2 g of amoxicillin and 8 mg of placebo; Group 3 (G3) included a prophylactic dose of 8 mg of dexamethasone and 2 g of placebo and; Group 4 (G4) placebo.
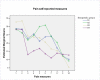
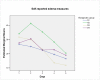
Results: Fifty patients were included. It was observed one case of alveolar infection (2%) and two of alveolar osteitis (4%) resulting in three PC (6%). No statistical differences were observed between therapeutic groups for development of PC, trismus, pain and edema. The use of antibiotics showed an absolute risk reduction (ARR) for PC development of 3.52% and the number needed to treat (NNT) was 29.
Conclusion: Prophylactic antibiotics and corticoid in a single dose regimen did not bring any benefit on M3 surgeries.
Keywords: Amoxicillin; Antibiotic prophylaxis; Dexamethasone; Third molar surgery.
Figures
References
-
- Arteagoitia I, Diez A, Barbier L, Santamaria G, Santamaria J. Efficacy of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid in preventing infectious and inflammatory complications following impacted mandibular third molar extraction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100(1):e11–18. - PubMed
-
- Kunkel M, Kleis W, Morbach T, Wagner W. Severe third molar complications including death-lessons from 100 cases requiring hospitalization. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65(9):1700–1706. - PubMed
-
- Ren YF, Malmstrom HS. Effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis in third molar surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65(10):1909–1921. - PubMed
-
- Baqain ZH, Karaky AA, Sawair F, Khraisat A, Duaibis R, Rajab LD. Frequency estimates and risk factors for postoperative morbidity after third molar removal: a prospective cohort study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(11):2276–2283. - PubMed
-
- Bouloux GF, Steed MB, Perciaccante VJ. Complications of third molar surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2007;19(1):117–128. vii. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical