FIP200 regulates targeting of Atg16L1 to the isolation membrane
- PMID: 23392225
- PMCID: PMC3589088
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2013.6
FIP200 regulates targeting of Atg16L1 to the isolation membrane
Abstract
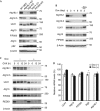
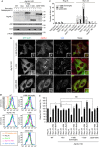
Autophagosome formation is a dynamic process that is strictly controlled by autophagy-related (Atg) proteins. However, how these Atg proteins are recruited to the autophagosome formation site or autophagic membranes remains poorly understood. Here, we found that FIP200, which is involved in proximal events, directly interacts with Atg16L1, one of the downstream Atg factors, in an Atg14- and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent manner. Atg16L1 deletion mutants, which lack the FIP200-interacting domain, are defective in proper membrane targeting. Thus, FIP200 regulates not only early events but also late events of autophagosome formation through direct interaction with Atg16L1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y (2011) The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27: 107–132 - PubMed
-
- Xie Z, Klionsky DJ (2007) Autophagosome formation: core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol 9: 1102–1109 - PubMed
-
- Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, Ohsumi Y (2009) Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 458–467 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Kubota Y, Sekito T, Ohsumi Y (2007) Hierarchy of Atg proteins in pre-autophagosomal structure organization. Genes Cells 12: 209–218 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

