A multi-biomarker score measures rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in the BeSt study
- PMID: 23392591
- PMCID: PMC3685330
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes362
A multi-biomarker score measures rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in the BeSt study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate a multi-biomarker disease activity (MBDA) score, a novel index based on 12 serum proteins, as a tool to guide management of RA patients.
Methods: A total of 125 patients with RA from the Behandel Strategieën study were studied. Clinical data and serum samples were available from 179 visits, 91 at baseline and 88 at year 1. In each serum sample, 12 biomarkers were measured by quantitative multiplex immunoassays and the concentrations were used as input to a pre-specified algorithm to calculate MBDA scores.
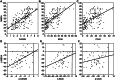
Results: MBDA scores had significant correlation with DAS28-ESR (Spearman's ρ = 0.66, P < 0.0001) and also correlated with simplified disease activity index, clinical disease activity index and HAQ Disability Index (all P < 0.0001). Changes in MBDA between baseline and year 1 were also correlated with changes in DAS28-ESR (ρ = 0.55, P < 0.0001). Groups stratified by European League Against Rheumatism disease activity (DAS28-ESR ≤ 3.2, 3.2-5.1 and > 5.1) had significantly different MBDA scores (P < 0.0001) and MBDA score could discriminate ACR/EULAR Boolean remission with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.83 (P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: The MBDA score reflects current clinical disease activity and can track changes in disease activity over time.
Keywords: bioinformatics; biomarkers; cytokines and inflammatory mediators; disability evaluation; molecular biology; outcome measures; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376:1094–108. - PubMed
-
- Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3381–90. - PubMed
-
- Grigor C, Capell H, Stirling A, et al. Effect of a treatment strategy of tight control for rheumatoid arthritis (the TICORA study): a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;364:263–9. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka E, Mannalithara A, Inoue E, et al. Efficient management of rheumatoid arthritis significantly reduces long-term functional disability. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1153–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

