A mutant prion protein sensitizes neurons to glutamate-induced excitotoxicity
- PMID: 23392670
- PMCID: PMC3711660
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3406-12.2013
A mutant prion protein sensitizes neurons to glutamate-induced excitotoxicity
Abstract
Growing evidence suggests that a physiological activity of the cellular prion protein (PrP(C)) plays a crucial role in several neurodegenerative disorders, including prion and Alzheimer's diseases. However, how the functional activity of PrP(C) is subverted to deliver neurotoxic signals remains uncertain. Transgenic (Tg) mice expressing PrP with a deletion of residues 105-125 in the central region (referred to as ΔCR PrP) provide important insights into this problem. Tg(ΔCR) mice exhibit neonatal lethality and massive degeneration of cerebellar granule neurons, a phenotype that is dose dependently suppressed by the presence of wild-type PrP. When expressed in cultured cells, ΔCR PrP induces large, ionic currents that can be detected by patch-clamping techniques. Here, we tested the hypothesis that abnormal ion channel activity underlies the neuronal death seen in Tg(ΔCR) mice. We find that ΔCR PrP induces abnormal ionic currents in neurons in culture and in cerebellar slices and that this activity sensitizes the neurons to glutamate-induced, calcium-mediated death. In combination with ultrastructural and biochemical analyses, these results demonstrate a role for glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in PrP-mediated neurodegeneration. A similar mechanism may operate in other neurodegenerative disorders attributable to toxic, β-rich oligomers that bind to PrP(C).
Figures
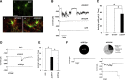

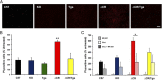
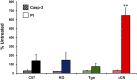

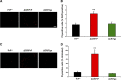
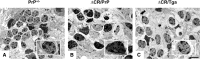

References
-
- Aguzzi A, Heikenwalder M, Polymenidou M. Insights into prion strains and neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:552–561. - PubMed
-
- Balducci C, Beeg M, Stravalaci M, Bastone A, Sclip A, Biasini E, Tapella L, Colombo L, Manzoni C, Borsello T, Chiesa R, Gobbi M, Salmona M, Forloni G. Synthetic amyloid-beta oligomers impair long-term memory independently of cellular prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:2295–2300. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biasini E, Harris DA. Targeting the cellular prion protein to treat neurodegeneration. Future Med Chem. 2012;4:1655–1658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30 NS063547/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065244/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- TCR08005/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- T32GM007200/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052526/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG00001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS040975/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040975/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- TCR08002/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- NS063547/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG000001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG025062/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS052526/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007200/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025062/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
