Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1)
- PMID: 23394211
- PMCID: PMC4057151
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11454
Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1)
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and serious problem affecting millions and causing death and disability for many. In 2012, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes completed the first ever, international, multidisciplinary, clinical practice guideline for AKI. The guideline is based on evidence review and appraisal, and covers AKI definition, risk assessment, evaluation, prevention, and treatment. In this review we summarize key aspects of the guideline including definition and staging of AKI, as well as evaluation and nondialytic management. Contrast-induced AKI and management of renal replacement therapy will be addressed in a separate review. Treatment recommendations are based on systematic reviews of relevant trials. Appraisal of the quality of the evidence and the strength of recommendations followed the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach. Limitations of the evidence are discussed and a detailed rationale for each recommendation is provided.
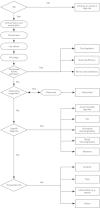
Figures

References
-
- KDIGO AKI Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;17:1–138.
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes. http://www.kdigo.org
-
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines: Online Appendix F. http://www.kdigo.org/clinical_practice_guidelines/AKI.php
-
- Uhlig K, Macleod A, Craig J, Lau J, Levey AS, Levin A, Moist L, Steinberg E, Walker R, Wanner C, Lameire N, Eknoyan G. Grading evidence and recommendations for clinical practice guidelines in nephrology. A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2006;17:2058–2065. - PubMed
-
- Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schünemann HJ, Edejer TT, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW Jr, Zaza S. GRADE Working Group. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2004;17:1490. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

