Severe strongyloidiasis: a systematic review of case reports
- PMID: 23394259
- PMCID: PMC3598958
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-78
Severe strongyloidiasis: a systematic review of case reports
Abstract
Background: Strongyloidiasis is commonly a clinically unapparent, chronic infection, but immuno suppressed subjects can develop fatal disease. We carried out a review of literature on hyperinfection syndrome (HS) and disseminated strongyloidiasis (DS), in order to describe the most challenging aspects of severe strongyloidiasis.
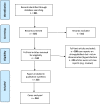
Methods: We conducted a structured search using PubMed to collect case reports and short case series on HS/DS published from 1991 to 2011. We restricted search to papers in English, Spanish, Italian and French. Case reports were classified as HS/DS according to given definitions.
Results: Records screened were 821, and 311 were excluded through titles and abstract evaluation. Of 510 full-text articles assessed for eligibility, 213 were included in qualitative analysis. As some of them were short case series, eventually the number of cases analyzed was 244.Steroids represented the main trigger predisposing to HS and DS (67% cases): they were mostly administered to treat underlying conditions (e.g. lymphomas, rheumatic diseases). However, sometimes steroids were empirically prescribed to treat signs and symptoms caused by unsuspected/unrecognized strongyloidiasis. Diagnosis was obtained by microscopy examination in 100% cases, while serology was done in a few cases (6.5%). Only in 3/29 cases of solid organ/bone marrow transplantation there is mention of pre-transplant serological screening. Therapeutic regimens were different in terms of drugs selection and combination, administration route and duration. Similar fatality rate was observed between patients with DS (68.5%) and HS (60%).
Conclusions: Proper screening (which must include serology) is mandatory in high - risk patients, for instance candidates to immunosuppressive medications, currently or previously living in endemic countries. In some cases, presumptive treatment might be justified. Ivermectin is the gold standard for treatment, although the optimal dosage is not clearly defined in case of HS/DS.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Strongyloidiasis. http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/diseases/strongyloidiasis/en/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials