Lipoxygenase: an emerging target for stroke therapy
- PMID: 23394536
- PMCID: PMC3676892
- DOI: 10.2174/18715273112119990053
Lipoxygenase: an emerging target for stroke therapy
Abstract
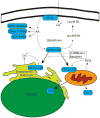
Neuroprotection as approach to stroke therapy has recently seen a revival of sorts, fueled in part by the continuing necessity to improve acute stroke care, and in part by the identification of novel drug targets. 12/15- Lipoxygenase (12/15-LOX), one of the key enzymes of the arachidonic acid cascade, contributes to both neuronal cell death and vascular injury. Inhibition of 12/15-LOX may thus provide multifactorial protection against ischemic injury. Targeting 12/15-LOX and related eicosanoid pathways is the subject of this brief review.
Conflict of interest statement
Support from the National Institutes of Health (R01NS049430 and R01NS069939) is gratefully acknowledged. A patent on the use of LOXBlock inhibitors to treat stroke has been applied for (U.S. Patent Application No.: 12/671,567).
Figures
References
-
- Shuaib A, Lees KR, Lyden P, Grotta J, Davalos A, Davis SM, Diener HC, Ashwood T, Wasiewski WW, Emeribe U. NXY-059 for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:562–71. - PubMed
-
- Quaegebeur A, Lange C, Carmeliet P. The neurovascular link in health and disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuron. 2011;71:406–24. - PubMed
-
- Lau A, Tymianski M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflugers Arch. 2010;460:525–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
