Novel R-roscovitine NO-donor hybrid compounds as potential pro-resolution of inflammation agents
- PMID: 23394865
- PMCID: PMC3898921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.01.009
Novel R-roscovitine NO-donor hybrid compounds as potential pro-resolution of inflammation agents
Abstract
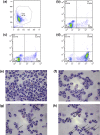
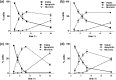
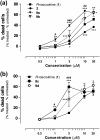
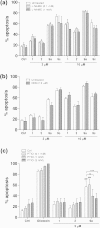
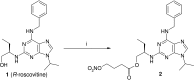
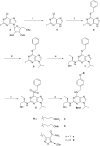
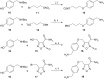
Neutrophils play a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of multiple human inflammatory diseases. Novel pharmacological strategies which drive neutrophils to undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis) have been shown to facilitate the resolution of inflammation. Both the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKi) R-roscovitine and nitric oxide (NO) have been shown to enhance apoptosis of neutrophils and possess pro-resolution of inflammation properties. In order to search for new multi-target pro-resolution derivatives, here we describe the design, synthesis and investigation of the biological potential of a small series of hybrid compounds obtained by conjugating R-roscovitine with two different NO-donor moieties (compounds 2, 9a, 9c). The synthesized compounds were tested as potential pro-resolution agents, with their ability to promote human neutrophil apoptosis evaluated. Both compound 9a and 9c showed an increased pro-apoptotic activity when compared with either R-roscovitine or structurally related compounds devoid of the ability to release NO (des-NO analogues). Inhibition of either NO-synthase or soluble guanylate cyclase did not affect the induction of apoptosis by the R-roscovitine derivatives, similar to that reported for other classes of NO-donors. In contrast the NO scavenger PTIO prevented the enhanced apoptosis seen with compound 9a over R-roscovitine. These data show that novel compounds such as CDKi-NO-donor hybrids may have additive pro-resolution of inflammation effects.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor drugs as potential novel anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution agents.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;158(4):1004-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00402.x. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19775281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor R-roscovitine down-regulates Mcl-1 to override pro-inflammatory signalling and drive neutrophil apoptosis.Eur J Immunol. 2010 Apr;40(4):1127-38. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939664. Eur J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20127676
-
Effects of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor R-roscovitine on eosinophil survival and clearance.Clin Exp Allergy. 2011 May;41(5):673-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03680.x. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21255143
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors enhance the resolution of inflammation by promoting inflammatory cell apoptosis.Nat Med. 2006 Sep;12(9):1056-64. doi: 10.1038/nm1468. Epub 2006 Sep 3. Nat Med. 2006. PMID: 16951685
-
Role of neutrophil apoptosis in the resolution of inflammation.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Sep 1;10:1731-48. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.169. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20842319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural elucidation and physiologic functions of specialized pro-resolving mediators and their receptors.Mol Aspects Med. 2017 Dec;58:114-129. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Mol Aspects Med. 2017. PMID: 28336292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating inflammation and infection in the 21st century: new hints from decoding resolution mediators and mechanisms.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1273-1288. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601222R. Epub 2017 Jan 13. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28087575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation Resolution and the Induction of Granulocyte Apoptosis by Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Drugs.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 19;10:55. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00055. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30886578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

