Nutrient sensing, metabolism, and cell growth control
- PMID: 23395268
- PMCID: PMC3587157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.019
Nutrient sensing, metabolism, and cell growth control
Abstract
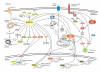
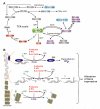
Cell growth is regulated by coordination of both extracellular nutrients and intracellular metabolite concentrations. AMP-activated kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 serve as key molecules that sense cellular energy and nutrients levels, respectively. In addition, the members of the dioxygenase family, including prolylhydroxylase, lysine demethylase, and DNA demethylase, have emerged as possible sensors of intracellular metabolic status. The interplay among nutrients, metabolites, gene expression, and protein modification are involved in the coordination of cell growth with extracellular and intracellular conditions.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bentzinger CF, Romanino K, Cloetta D, Lin S, Mascarenhas JB, Oliveri F, Xia J, Casanova E, Costa CF, Brink M, et al. Skeletal muscle-specific ablation of raptor, but not of rictor, causes metabolic changes and results in muscle dystrophy. Cell Metab. 2008;8:411–424. - PubMed
-
- Binda M, Peli-Gulli MP, Bonfils G, Panchaud N, Urban J, Sturgill TW, Loewith R, De Virgilio C. The Vam6 GEF controls TORC1 by activating the EGO complex. Mol Cell. 2009;35:563–573. - PubMed
-
- Bonfils G, Jaquenoud M, Bontron S, Ostrowicz C, Ungermann C, De Virgilio C. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase controls TORC1 via the EGO complex. Mol Cell. 2012;46:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Browne GJ, Finn SG, Proud CG. Stimulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase leads to activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and to its phosphorylation at a novel site, serine 398. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:12220–12231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

