Noncanonical EF-hand motif strategically delays Ca2+ buffering to enhance cardiac performance
- PMID: 23396207
- PMCID: PMC3727912
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3079
Noncanonical EF-hand motif strategically delays Ca2+ buffering to enhance cardiac performance
Abstract
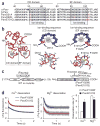
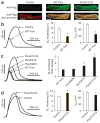
EF-hand proteins are ubiquitous in cell signaling. Parvalbumin (Parv), the archetypal EF-hand protein, is a high-affinity Ca(2+) buffer in many biological systems. Given the centrality of Ca(2+) signaling in health and disease, EF-hand motifs designed to have new biological activities may have widespread utility. Here, an EF-hand motif substitution that had been presumed to destroy EF-hand function, that of glutamine for glutamate at position 12 of the second cation binding loop domain of Parv (ParvE101Q), markedly inverted relative cation affinities: Mg(2+) affinity increased, whereas Ca(2+) affinity decreased, forming a new ultra-delayed Ca(2+) buffer with favorable properties for promoting cardiac relaxation. In therapeutic testing, expression of ParvE101Q fully reversed the severe myocyte intrinsic contractile defect inherent to expression of native Parv and corrected abnormal myocardial relaxation in diastolic dysfunction disease models in vitro and in vivo. Strategic design of new EF-hand motif domains to modulate intracellular Ca(2+) signaling could benefit many biological systems with abnormal Ca(2+) handling, including the diseased heart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Clapham DE. Calcium signaling. Cell. 2007;131:1047–1058. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 2002;415:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Kaye DM, Hoshijima M, Chien KR. Reversing advanced heart failure by targeting Ca2+ cycling. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:13–28. - PubMed
-
- Kass DA, Bronzwaer JG, Paulus WJ. What mechanisms underlie diastolic dysfunction in heart failure? Circ Res. 2004;94:1533–1542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

