Essential Staphylococcus aureus toxin export system
- PMID: 23396209
- PMCID: PMC3594369
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3047
Essential Staphylococcus aureus toxin export system
Abstract
Widespread antibiotic resistance among important bacterial pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus calls for alternative routes of drug development. Interfering with crucial virulence determinants is considered a promising new approach to control bacterial infection. Phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) are peptide toxins with multiple key roles in pathogenesis and have a major impact on the ability of highly virulent S. aureus to cause disease. However, targeting PSMs for therapeutic intervention is hampered by their multitude and diversity. Here we report that an ATP-binding cassette transporter with previously unknown function is responsible for the export of all PSMs, thus representing a single target for complete obstruction of PSM production. The transporter had a strong effect on virulence phenotypes, such as neutrophil lysis, and the extent of its effect on the development of S. aureus infection was similar to that of the sum of all PSMs. Notably, the transporter was essential for bacterial growth. Furthermore, it contributed to producer immunity toward secreted PSMs and defense against PSM-mediated bacterial interference. Our study reveals a noncanonical, dedicated secretion mechanism for an important class of toxins and identifies this mechanism as a comprehensive potential target for the development of drugs to efficiently inhibit the growth and virulence of pathogenic staphylococci.
Figures

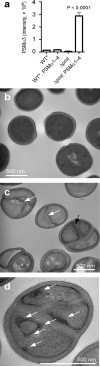
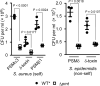
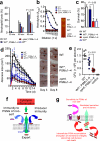
Comment in
-
Bacterial toxins: Exposing the exporter.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Apr;11(4):222-3. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2995. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23456044 No abstract available.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins, hellhounds from the staphylococcal virulence-factor pandemonium.Trends Microbiol. 2013 Jul;21(7):313-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 May 14. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23684152
Similar articles
-
Phenol-soluble modulins, hellhounds from the staphylococcal virulence-factor pandemonium.Trends Microbiol. 2013 Jul;21(7):313-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 May 14. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23684152
-
Multidrug-Resistance Transporter AbcA Secretes Staphylococcus aureus Cytolytic Toxins.J Infect Dis. 2016 Jan 15;213(2):295-304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv376. Epub 2015 Jul 9. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26160745
-
Direct and synergistic hemolysis caused by Staphylococcus phenol-soluble modulins: implications for diagnosis and pathogenesis.Microbes Infect. 2012 Apr;14(4):380-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.11.013. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22178792 Free PMC article.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Mar;304(2):164-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.11.019. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24447915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins and staphylococcal infection.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Oct;11(10):667-73. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3110. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24018382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Growth Stage on the Characterization of Enterotoxin A-Producing Staphylococcus aureus-Derived Membrane Vesicles.Microorganisms. 2022 Mar 6;10(3):574. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030574. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35336149 Free PMC article.
-
The role of bacterial transport systems in the removal of host antimicrobial peptides in Gram-negative bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022 Nov 2;46(6):fuac032. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuac032. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35749576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liposomal Therapy Attenuates Dermonecrosis Induced by Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Targeting α-Type Phenol-Soluble Modulins and α-Hemolysin.EBioMedicine. 2018 Jul;33:211-217. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.06.016. Epub 2018 Jun 20. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 29936135 Free PMC article.
-
The psmα locus regulates production of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin during infection.Infect Immun. 2014 Aug;82(8):3350-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00089-14. Epub 2014 May 27. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24866799 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Phenol-Soluble Modulins Impair Interleukin Expression in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Infect Immun. 2016 May 24;84(6):1682-1692. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01330-15. Print 2016 Jun. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27001539 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

