US in pubalgia
- PMID: 23396870
- PMCID: PMC3558068
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jus.2011.06.005
US in pubalgia
Abstract
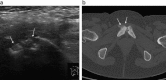
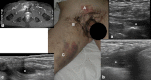
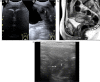
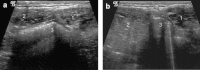
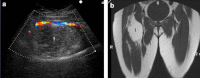
There is considerable confusion over the word "pubalgia" with regard to the definition and the etiological causes of this condition. The term pubalgia should be used to indicate disabling pain affecting the pubic region in people who practise sports. Pubalgia affects 10% of those who practise sports and it is particularly prevalent in football players. According to the literature, about 40% of cases of pubalgia are caused by overuse of the symphysis pubis with progressive lesions affecting the rectus abdominal muscles, adductors (rectal-adductor syndrome) and the symphysis itself (osteitis pubis and joint injury). An initial study of the tendons is carried out by ultrasound (US) whereas magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) should be performed to study the bones and joints.Another 40% of cases of pubalgia are caused by "sports hernia" defined as anteroinferior abdominal wall insufficiency. These alterations can only be identified at dynamic US examination.About 20% of cases of pubalgia are caused by diseases of the neighboring structures or joints such as diseases of the hip, iliopsoas, hamstring, sacred iliac or nerves, or by urogenital diseases.
SommarioVi è notevole confusione circa la parola “pubalgia”, sia per quanto riguarda la sua definizione sia per quanto riguarda le sue cause etiologiche. Il termine di pubalgia dovrebbe essere utilizzato per indicare una sintomatologia dolorosa, invalidante che interessa la regione pubica di chi pratica attività sportiva. Sono interessati il 10% di chi pratica attività sportiva con prevalenza per il footbal. Dalla revisione della letteratura circa il 40% delle pubalgie sono da ricondurre a sovraccarico funzionale sulla sinfisi pubica con lesioni progressive che interessano i retti addominali, gli adduttori (sindrome retto-adduttoria), e la sinfisi stessa (osteite pubica e danno alla articolazione). Lo studio dei tendini trova nella ecografia il primo approccio diagnostico riservando alla RM lo studio della componente ossea e articolare.Un altro 40% dei casi di pubalgia riconosce la causa etiologica nella “sport hernia”, definibile come una insufficienza della parete addominale antero-inferiore. La diagnostica ecografica è l’unica in grado di rilevare tali alterazioni che necessitano per essere individuate un esame dinamico.Infine in circa il 20% dei casi la pubalgia è causata da patologie di strutture o apparati limitrofi: patologia dell’anca, dell’ileo-psoas, degli hamstring, della sacro iliaca o dei nervi, fino alle patologie urogenitali.
Keywords: Pubalgia; Sports hernia; Ultrasound.
Figures












Similar articles
-
>Imaging Assessment of the Pubis in Soccer Players.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2019 Apr;54(2):118-127. doi: 10.1016/j.rbo.2017.12.012. Epub 2019 May 10. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31363256 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial Commentary: Managing Hip Pain, Athletic Pubalgia, Sports Hernia, Core Muscle Injury, and Inguinal Disruption Requires Diagnostic and Therapeutic Expertise.Arthroscopy. 2021 Jul;37(7):2391-2392. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2021.04.027. Arthroscopy. 2021. PMID: 34226017
-
Athletic Pubalgia (Sports Hernia): Presentation and Treatment.Arthroscopy. 2020 Dec;36(12):2952-2953. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.09.022. Arthroscopy. 2020. PMID: 33276883
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of athletic pubalgia and the sports hernia: current understanding and practice.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2013 Feb;21(1):97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2012.09.008. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2013. PMID: 23168185 Review.
-
Groin Injuries (Athletic Pubalgia) and Return to Play.Sports Health. 2016 Jul;8(4):313-23. doi: 10.1177/1941738116653711. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Sports Health. 2016. PMID: 27302153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing Conservative Management of Groin Pain in Athletes: Insights from a Narrative Review.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;15(3):411. doi: 10.3390/life15030411. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40141755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High insertion of conjoint tendon is associated with inguinal-related groin pain: a MRI study.Eur Radiol. 2020 Mar;30(3):1517-1524. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06466-4. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31728693
-
Ultrasound imaging of the axilla.Insights Imaging. 2023 May 11;14(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01430-9. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37166516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulse-dose radiofrequency treatment in pain management-initial experience.Skeletal Radiol. 2018 May;47(5):609-618. doi: 10.1007/s00256-017-2854-8. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Skeletal Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29275456 Review.
-
Osteitis pubis in elite athletes: Diagnostic and therapeutic approach.World J Orthop. 2015 Oct 18;6(9):672-9. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i9.672. eCollection 2015 Oct 18. World J Orthop. 2015. PMID: 26495244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Irshad K., Feldman L.S., Lavoie C., Lacroix V.J., Mulder D.S., Brown R.A. Operative management of “hockey groin syndrome”: 12 years of experience in national hockey league players. Surgey. 2001;130:759–764. - PubMed
-
- Puig P.L., Trouve P., Savalli L. Pubalgia: from diagnosis to return to the sport field. Ann Readapt Med Phys. 2004;47:356–364. - PubMed
-
- Zoga A.C., Kavanagh E.C., Omar I.M., Morrison W.B., Koulouris G., Lopez H. Athletic pubalgia and the “sports hernia”: MR imaging findings. Radiology. 2008;247:797–807. - PubMed
-
- Vidalin H., Neouze G., Petit Brunet-Guedi E. Prise en charge chirurgicale des pubalgies du sportif. J Traumatol Sport. 2004;21:166–173.
-
- Campanelli G. Pubic inguinal pain syndrome: the so-called sports hernia. Hernia. 2010;14:1–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
