Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
- PMID: 23396938
- PMCID: PMC3604492
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008505
Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
Abstract
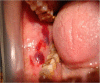
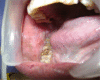
Angina bullosa haemorrhagica is the term used to describe benign subepithelial oral mucosal blisters filled with blood that are not attributable to a systemic disorder or haemostatic defect. It is a very rare condition. Elderly patients are usually affected and lesions heal spontaneously without scarring. The pathogenesis is unknown, although it may be a multifactorial phenomenon. Trauma seems to be the major provoking factor and long-term use of steroid inhalers has also been implicated in the disease. We present a 50-year-old patient with angina bullosa haemorrhagica. Trauma by sharp cusp of adjacent tooth and metal crown were identified as aetiological factors in this case. Lesions healed after removal of the metal crown and rounding of the cusp. Therefore, recognition of the lesion is of great importance to dentists, to avoid misdiagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Giuliani M, Favia GF, Miani CM. Angina bullosa haemorrhagica: presentation of eight new cases and a review of the literature. Oral Dis 2002;8:54–8 - PubMed
-
- Grinspan D. Hemoflictenosis bucal recidivante. In: Enfermedades de la boca. Vol III Buenos Aires: Mundi Philippe Sionneau, 1976:1502–5
-
- Grinspan D. Angina bullosa haemorrhagica. Int J Dermatol 1999;38:525–8 - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto K, Fujimoto M, Inoue M, et al. Angina bullosa hemorrhagica of soft palate: report of 11 cases and litreture review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2006;64:1433–6 - PubMed
-
- Horie N, Kawano R, Inaba J, et al. Angina bullosa hemorrhagica of soft palate: a clinical study of 16 cases. J Oral Sci 2008;50:33–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources