US imaging in operated tendons
- PMID: 23396989
- PMCID: PMC3558105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jus.2011.11.001
US imaging in operated tendons
Abstract
Ultrasound (US) plays an essential role in the follow-up of operated tendons. The US operator must keep in mind three main elements: healing of traumatic injuries of the tendons seems to follow the biological model of histologic healing, surgical repair of a tendon rupture improves the structural parameters of the operated tendon, but it does not grant restitutio ad integrum, and US findings therefore seem poorly correlated with the functional evolution.Before examination, the US operator should be familiar with the nature of the tendon injury that has led to surgery including location, severity, time elapsed between tendon injury and surgical repair, surgical technique, postoperative course and possible complications. US findings in operated as well as non-operated tendons depend on several factors: morphology, structure, vascularization of the tendon, mobility of the tendon and mobility of the peritendinous tissues. Particular features are therefore considered according to the location: shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, knee, ankle and foot. Interpretation of the US image requires knowledge of the surgical technique and "normal" postoperative appearance of the operated tendon in order to detect pathological findings such as thinning, persistent fluid collections within or around the tendon, persistent hypervascularization, intratendinous calcifications and adhesions.
SommarioL’ecografia riveste un ruolo essenziale nel follow-up dei tendini operati. Nella sua esecuzione l’ecografista deve tenere ben presenti tre punti: la cicatrizzazione delle lesioni traumatiche dei tendini, all’esame ecografico, sembra seguire il modello biologico di cicatrizzazione istologica, la riparazione chirurgica di una rottura tendinea migliora i parametri strutturali del tendine operato, ma non apporta una restitutio ad integrum, i segni ecografici sembrano mal correlati all’evoluzione funzionale.Prima di iniziare l’esame l’ecografista deve conoscere alcuni dati: la natura della lesione tendinea per cui è stato realizzato l’intervento chirurgico, la sede, la gravità, l’intervallo temporaneo tra la lesione tendinea e la sua riparazione chirurgica, il tipo di tecnica, il decorso e le eventuali complicanze post-operatorie.Come per il tendine non operato la semiotica ecografica è basata su vari elementi: morfologia, struttura, vascolarizzazione del tendine, sua mobilità e mobilità dei tessuti peritendinei.Vengono quindi presi in considerazione problemi particolari a seconda della sede: spalla, gomito, polso e mano, ginocchio, caviglia e piede.L’interpretazione delle immagini dell’ecografia richiede la conoscenza della tecnica operatoria e dell’aspetto “normale” del tendine operato.È importante mettere in evidenza i reperti peggiorativi quali: assottigliamento, raccolta liquida intra o peritendea persistente, ipervascularizzazione persistente, calcificazioni intratendinee, aderenze.
Keywords: Operated Tendons; Tendons; Ultrasound.
Figures







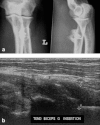
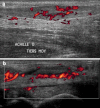




References
-
- Brasseur J.L., Nicolaon L., Saillant G. Echographie des tendons opérés. In: Bard H., Cotten A., Rodineau J., Saillant G., Railhac J.J., editors. Tendons et enthèses, Monographie du GETROA-GEL, Sauramps. 2003. pp. 379–388.
-
- Peetrons P., Vanderhofstadt A. Echographie des tendons traités. In: Brasseur J.L., Dion E., Zeitoun-Eiss D., editors. Actualités en échographie de l’appareil locomoteur Sauramps. 2001. pp. 183–196.
-
- Drapé J.L., Cohen M. Imagerie des complications des tendons opérés. In: Drapé J.L., Blum A., Cyteval C., Pham T., Dautel G., Boutry N., Godefroy Poignet et Main D., editors. Monographie du GETROA-GEL, Sauramps. 2009. pp. 501–508.
-
- Fantino O., Besse J.L., Moyen B., Tran Minh V.A. Imagerie du tendon calcanéen opéré: Echographie et IRM. In: Bard H., Cotten A., Rodineau J., Saillant G., Railhac J.J., editors. Tendons et enthèses, Monographie du GETROA-GEL, Sauramps. 2003. pp. 395–411.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
