First-in-human phase 1/2a trial of CRLX101, a cyclodextrin-containing polymer-camptothecin nanopharmaceutical in patients with advanced solid tumor malignancies
- PMID: 23397498
- PMCID: PMC3774600
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-012-9921-8
First-in-human phase 1/2a trial of CRLX101, a cyclodextrin-containing polymer-camptothecin nanopharmaceutical in patients with advanced solid tumor malignancies
Abstract
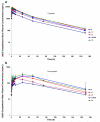
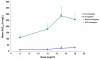
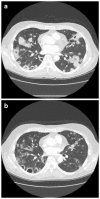
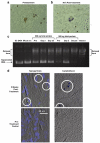
Patients with advanced solid malignancies were enrolled to an open-label, single-arm, dose-escalation study, in which CRLX101 was administered intravenously over 60 min among two dosing schedules, initially weekly at 6, 12, and 18 mg/m(2) and later bi-weekly at 12, 15, and 18 mg/m(2). The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was determined at 15 mg/m(2) bi-weekly, and an expansion phase 2a study was completed. Patient samples were obtained for pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) assessments. Response was evaluated per RECIST criteria v1.0 every 8 weeks. Sixty-two patients (31 male; median age 63 years, range 39-79) received treatment. Bi-weekly dosing was generally well tolerated with myelosuppression being the dose-limiting toxicity. Among all phase 1/2a patients receiving the MTD (n = 44), most common grade 3/4 adverse events were neutropenia and fatigue. Evidence of systemic plasma exposure to both the polymer-conjugated and unconjugated CPT was observed in all treated patients. Mean elimination unconjugated CPT Tmax values ranged from 17.7 to 24.5 h, and maximum plasma concentrations and areas under the curve were generally proportional to dose for both polymer-conjugated and unconjugated CPT. Best overall response was stable disease in 28 patients (64 %) treated at the MTD and 16 (73 %) of a subset of NSCLC patients. Median progression-free survival (PFS) for patients treated at the MTD was 3.7 months and for the subset of NSCLC patients was 4.4 months. These combined phase 1/2a data demonstrate encouraging safety, pharmacokinetic, and efficacy results. Multinational phase 2 clinical development of CRLX101 across multiple tumor types is ongoing.
Figures


References
-
- Gaur S, Chen L, Yen T, et al. Preclinical study of the cyclodextrin-polymer conjugate of camptothecin for the treatment of gastric cancer. Nanomedicine. 2012;8:721–730. - PubMed
-
- Schluep T, Cheng J, Khin KT, et al. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of the camptothecin-polymer conjugate IT-101 in rats and tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006;57:654–662. - PubMed
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Han Z, Wei W, Dunaway S, et al. Role of p21 in apoptosis and senescence of human colon cancer cells treated with camptothecin. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:17154–17160. - PubMed
-
- Magrini R, Bhonde MR, Hanski ML, et al. Cellular effects of CPT-11 on colon carcinoma cells: dependence on p53 and hMLH1 status. Int J Cancer. 2002;101:23–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

