Intense exercise training is not effective to restore the endothelial NO-dependent relaxation in STZ-diabetic rat aorta
- PMID: 23399712
- PMCID: PMC3599941
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-32
Intense exercise training is not effective to restore the endothelial NO-dependent relaxation in STZ-diabetic rat aorta
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to examine the effects of intense physical training on vascular function in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. We focused on the endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR) induced by acetylcholine (ACh) and stable ADP adenosine-5'- O - (2-thiodiphosphate) (ADPβS).
Methods: Control or diabetic male Wistar rats (n=44) were randomly assigned to sedentary or trained groups. The training program consisted in a regular period of running on a treadmill during 8 weeks (10° incline and up to 25 m/min, 60 min/day). The reactivity of isolated thoracic aorta rings of healthy, diabetic and/or trained has been tested.
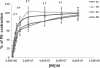
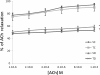
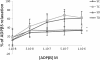
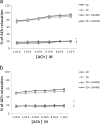
Results: ACh and ADPβS-induced EDR were observed in phenylephrine (PE) pre-contracted vessels. As compared to sedentary control group, diabetic rats showed an increase in PE-induced contraction and a decrease in ACh and ADPβS-induced EDR (p<0.05). Moreover, there were no increase in ACh and ADPβS-induced EDR in diabetic rats. N-Nitro-L-Arginine Methyl Ester inhibited the nitric oxide synthase in diabetic and control rats, thereby resulting in a strong inhibition of the EDR induced by ACh and ADPβS (10-6 M).
Conclusion: Diabetes induced an endothelium dysfunction. Nevertheless, our intense physical training was not effective to restore the aorta endothelial function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pioglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, restores endothelial function in aorta of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Apr 1;66(1):150-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.12.025. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15769458
-
Effect of dietary docosahexaenoic acid on the endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in diabetic rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005 Mar;32(3):184-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2005.04169.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15743401
-
Characteristics of impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation of rat aorta after streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999 Sep;20(9):844-50. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999. PMID: 11245095
-
Interleukin-2 protects against endothelial dysfunction induced by high glucose levels in rats.Vascul Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;45(6):374-82. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2006.06.002. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Vascul Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16837248
-
Endothelial function and exercise training: evidence from studies using animal models.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006 Mar;38(3):445-54. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000191187.24525.f2. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006. PMID: 16540831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resistance exercise restores endothelial function and reduces blood pressure in type 1 diabetic rats.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2014 Jul;103(1):25-32. doi: 10.5935/abc.20140087. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25120082 Free PMC article.
-
The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist anakinra improves endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Dec 18;13:158. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0158-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 25518980 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in the neural circuits from peripheral afferents to the spinal cord: possible implications for diabetic polyneuropathy in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Jan 29;8:6. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00006. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 24523675 Free PMC article.
-
Lysozyme-Antimicrobial Peptide Fusion Protein Promotes the Diabetic Wound Size Reduction in Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Diabetic Rats.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 23;24:8449-8458. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912596. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30468157 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide accelerates wound healing in diabetic rats.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):5097-104. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pellegrin M, Bertholot A, Houdayer C, Gaume V, Deckert V, Laurent P. New insights into the vascular mechanisms underlying the beneficial effect of swimming training on the endothelial vasodilator function in apolipo-protein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 2007;190:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

