Effect of CD40 and sCD40L on renal function and survival in patients with renal artery stenosis
- PMID: 23399713
- PMCID: PMC3783956
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00685
Effect of CD40 and sCD40L on renal function and survival in patients with renal artery stenosis
Abstract
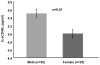
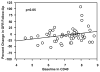
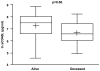
Activation of the CD40 receptor on the proximal tubular epithelium of the kidney results in fibrosis and inflammation in experimental models of kidney injury. Soluble CD40 ligand is released by activated platelets. The role of CD40-soluble CD40 ligand in patients with ischemic renal disease is unknown. Plasma levels of CD40 and soluble CD40 ligand were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in a single center cohort of 60 patients with renal artery stenosis recruited from Salford Royal Hospital, Manchester, United Kingdom. A natural log transformation of CD40 and soluble CD40 ligand was performed to normalize the data. Estimated glomerular filtration rate was used as the primary indicator of renal function. By univariate analysis, low baseline levels of circulating CD40 (R(2)=0.06; P<0.05) and baseline creatinine (R(2)=0.08; P=0.022) were associated with loss of kidney function at 1-year follow-up, whereas soluble CD40 ligand was not (R(2)=0.02; P=ns). In a multiple linear regression model, CD40 (P<0.02) and baseline creatinine (P<0.01) continued to be significantly associated with a decline in renal function (model R(2)=0.17; P<0.005). Baseline CD40 levels were somewhat lower in patients who died during follow-up (survivors, 7.3±0.9 pg/mL, n=48 versus nonsurvivors, 6.7±1.0 pg/mL, n=12; P=0.06). The CD40/soluble CD40 ligand signaling cascade may be a novel mechanism contributing to the development and progression of renal injury in patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis.
Figures
References
-
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. Cd40-cd40 ligand. Journal of leukocyte biology. 2000;67:2–17. - PubMed
-
- Antoniades C, Bakogiannis C, Tousoulis D, Antonopoulos AS, Stefanadis C. The cd40/cd40 ligand system: Linking inflammation with atherothrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:669–677. - PubMed
-
- Gaweco AS, Mitchell BL, Lucas BA, McClatchey KD, Van Thiel DH. Cd40 expression on graft infiltrates and parenchymal cd154 (cd40l) induction in human chronic renal allograft rejection. Kidney Int. 1999;55:1543–1552. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Nord EP. Il-8 amplifies cd40/cd154-mediated icam-1 production via the cxcr-1 receptor and p38-mapk pathway in human renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009;296:F438–445. - PubMed
-
- Pontrelli P, Rossini M, Infante B, et al. Rapamycin inhibits PAI-1 expression and reduces interstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis in chronic allograft nephropathy. Transplantation. 2008;85:125–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

