Ovarian hormones and the heterogeneous receptor mechanisms mediating the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol in female rats
- PMID: 23399883
- PMCID: PMC3864632
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32835efc5f
Ovarian hormones and the heterogeneous receptor mechanisms mediating the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol in female rats
Abstract
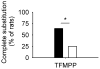
Past studies have suggested that progesterone-derived ovarian hormones contribute to the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol, particularly via progesterone metabolites that act at γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptors. It is unknown whether loss of ovarian hormones in women, for example, after menopause, may be associated with altered receptor mediation of the effects of ethanol. The current study measured the substitution of allopregnanolone, pregnanolone, pentobarbital, midazolam, dizocilpine, TFMPP, and RU 24969 in female sham and ovariectomized rats trained to discriminate 1.0 g/kg ethanol from water. The groups did not differ in the substitution of GABA(A)-positive modulators (barbiturates, benzodiazepines, neuroactive steroids) or the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist dizocilpine. Similarly, blood-ethanol concentration did not differ between the groups, and plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone, progesterone, pregnenolone, and deoxycorticosterone were unchanged 30 min after administration of 1.0 g/kg ethanol or water. However, substitution of neuroactive steroids and RU 24969, a 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)(1A/1B) receptor agonist, was lower than observed in previous studies of male rats, and TFMPP substitution was decreased in ovariectomized rats. Ovarian hormones appear to contribute to 5-HT receptor mediation of the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol in rats.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bowen CA, Purdy RH, Grant KA. Ethanol-like discriminative stimulus effects of endogenous neuroactive steroids: effects of ethanol training dose and dosing procedure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289:405–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

