Primary tumor PET/CT [¹⁸F]FDG uptake is an independent predictive factor for regional lymph node metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23399986
- PMCID: PMC3569669
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2012.0040
Primary tumor PET/CT [¹⁸F]FDG uptake is an independent predictive factor for regional lymph node metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the correlation between [¹⁸F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in a primary tumor and pathologic N stages, and to further analyze the possible risk factors contributing to the regional lymph node metastasis.
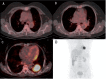
Patients and methods: Eighty patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who underwent positron emission tomography/computed tomography were enrolled in the study. The FDG uptake in the primary tumor was compared for the different N staging groups and further correlation was performed. The degree of FDG uptake in the primary tumor and other possible variables related to the incidence of lymph node metastasis were examined by univariate and logistic multivariate analysis. FDG uptake was quantitated using the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax).
Results: Statistically significant differences were found in the SUVmax of the primary tumors among different N staging groups (F = 4.124, P = 0.023), and the correlation between them was also statistically significant (r = 0.438, P = 0.000). Univariate analysis showed that blood tumor markers, primary tumor size, histologic grade, and SUVmax of the primary tumor were significantly associated with lymph node involvement. Logistic multivariate analysis showed that blood tumor makers and SUVmax of primary tumor might be considered as significant predictive factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with NSCLC.
Conclusion: Our results show that there is a significant relationship between the SUVmax of the primary tumor and the pathologic N stage of NSCLC. FDG uptake by the primary tumor may be an independent predictor of regional lymph node metastasis in patients with NSCLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of maximum standardized uptake value on fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography in predicting lymph node involvement in patients with primary non-small cell lung cancer.Anticancer Res. 2014 Feb;34(2):805-10. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24511016
-
Prognostic value of SUVmax and metabolic tumor volume on 18F-FDG PET/CT in early stage non-small cell lung cancer patients without LN metastasis.Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(6):3091-103. doi: 10.3233/BME-141131. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014. PMID: 25227018
-
An Investigation of the Relationship Between 18F-FDG PET/CT Parameters of Primary Tumors and Lymph Node Metastasis in Resectable Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(1):111-116. doi: 10.2174/1874471016666230829100703. Curr Radiopharm. 2024. PMID: 37644744
-
18F-FDG uptake by primary tumor as a predictor of intratumoral lymphatic vessel invasion and lymph node involvement in non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of a multicenter study.J Nucl Med. 2005 Feb;46(2):267-73. J Nucl Med. 2005. PMID: 15695786
-
Standardized Uptake Values in the Primary Lesions of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in FDG-PET/CT Can Predict Regional Lymph Node Metastases.Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;22 Suppl 3:S1388-93. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4564-6. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25900205
Cited by
-
FDG uptake of pulmonary lesions in synchronous primary lung cancers and lung metastases.Res Diagn Interv Imaging. 2024 Mar 8;9:100041. doi: 10.1016/j.redii.2024.100041. eCollection 2024 Mar. Res Diagn Interv Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39076580 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of pathological nodal involvement by CT-based Radiomic features of the primary tumor in patients with clinically node-negative peripheral lung adenocarcinomas.Med Phys. 2018 Jun;45(6):2518-2526. doi: 10.1002/mp.12901. Epub 2018 Apr 29. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29624702 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of upstaged N1 and N2 disease after curative resection in patients with clinical N0 non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Apr;11(4):1202-1212. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.04.30. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31179062 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Fluorine-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron-Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT) and Tumor Markers to Diagnose Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Retrospective and Prospective Study.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jun 2;26:e922675. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922675. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32483109 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning based on clinico-biological features integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics for distinguishing squamous cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma of lung.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 May;48(5):1538-1549. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-05065-6. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33057772 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
