Sedentary behavior and physical activity in youth with recent onset of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 23400602
- PMCID: PMC3581838
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2012-0620
Sedentary behavior and physical activity in youth with recent onset of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: With the rise of type 2 diabetes in youth, it is critical to investigate factors such as physical activity (PA) and time spent sedentary that may be contributing to this public health problem. This article describes PA and sedentary time in a large cohort of youth with type 2 diabetes and compares these levels with other large-scale investigations.
Methods: The Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth (TODAY) trial is a study in 699 youth, recruited from 15 US clinical centers, aged 10 to 17 years with <2 years of type 2 diabetes and a BMI ≥85th percentile.
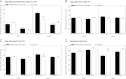
Results: In comparison with the subset of the NHANES cohort who were obese (BMI ≥95th percentile), TODAY youth spent significantly more time being sedentary (difference averaging 56 minutes per day; P < .001) as assessed by accelerometry. Although moderate to vigorous activity levels in both obese cohorts for all age groups were exceptionally low, younger TODAY boys were still significantly less active than similarly aged NHANES youth. Comparisons between the TODAY girls and other investigations suggest that the TODAY girls also had relatively lower PA and fitness levels.
Conclusions: Adolescents with type 2 diabetes from the large TODAY cohort appear to be less physically active and tend to spend more time being sedentary than similarly aged youth without diabetes identified from other large national investigations. Treatment efforts in adolescents with type 2 diabetes should include decreasing sitting along with efforts to increase PA levels.
Figures
References
-
- Data Resource Center. National survey of children’s health. Available at: www.nschdata.org/Content/Default.aspx. Accessed November 9, 2010
-
- Liese AD, D’Agostino RB, Jr, Hamman RF, et al. SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group . The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics. 2006;118(4):1510–1518 - PubMed
-
- Imperatore G, Cheng YJ, Williams DE, Fulton J, Gregg EW. Physical activity, cardiovascular fitness, and insulin sensitivity among U.S. adolescents: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2002. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(7):1567–1572 - PubMed
-
- Zeitler P, Epstein L, Grey M, et al. TODAY Study Group . Treatment options for type 2 diabetes in adolescents and youth: a study of the comparative efficacy of metformin alone or in combination with rosiglitazone or lifestyle intervention in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(2):74–87 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK61239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK61242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK61212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR014467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK61254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK61230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

