Increased circulation of galectin-3 in cancer induces secretion of metastasis-promoting cytokines from blood vascular endothelium
- PMID: 23401226
- PMCID: PMC3618858
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2940
Increased circulation of galectin-3 in cancer induces secretion of metastasis-promoting cytokines from blood vascular endothelium
Abstract
Purpose: Cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-6 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) are important metastasis promoters. This study has investigated the functional significance of the increased circulation of galectin-3, a common feature in patients with cancer and in particular those with metastasis, on cytokine secretion from the blood vascular endothelium in cancer.
Experimental design: The effects of galectin-3 on secretion of cytokines from human microvascular lung endothelial cells were assessed in vitro by cytokine array and in vivo in mice. The consequences of galectin-3-induced cytokine secretion on endothelial cell behaviors were determined, and the relationship between the levels of circulating galectin-3 and cytokines in patients with colorectal cancer with and without metastasis was investigated.
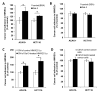
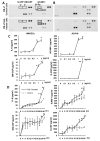
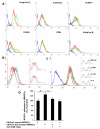
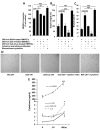
Results: Galectin-3 at pathologic concentrations found in patients with cancer induces secretion of IL-6, G-CSF, sICAM-1, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor from blood vascular endothelial cells in vitro and in mice. These cytokines autocrinely/paracrinely interact with the vascular endothelium to increase the expressions of endothelial cell surface adhesion molecules integrinα(v)β(1), E-selectin, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1, resulting in increased cancer cell-endothelial adhesion and increased endothelial cell migration and tubule formation. In patients with metastatic colon cancer, higher serum galectin-3 levels correlated significantly with increased serum G-CSF, IL-6, and sICAM1 concentrations.
Conclusion: The increased circulation of galectin-3 in patients with cancer induces secretion of several metastasis-promoting cytokines from the blood vascular endothelium that enhances endothelial cell activities in metastasis. Targeting the actions of circulating galectin-3 in patients with cancer therefore represents a promising therapeutic strategy to reduce metastasis and improve survival.
©2013 AACR.
Figures

References
-
- Liu FT, Rabinovich GA. Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:29–41. - PubMed
-
- Newlaczyl AU, Yu LG. Galectin-3--a jack-of-all-trades in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011;313:123–8. - PubMed
-
- Barrow H, Guo X, Wandall HH, Pedersen JW, Fu B, Zhao Q, et al. Serum galectin-2, -4, and -8 are greatly increased in colon and breast cancer patients and promote cancer cell adhesion to blood vascular endothelium. Clinical cancer research. 2011;17:7035–46. - PubMed
-
- Iurisci I, Tinari N, Natoli C, Angelucci D, Cianchetti E, Iacobelli S. Concentrations of galectin-3 in the sera of normal controls and cancer patients. Clinical cancer research. 2000;6:1389–93. - PubMed
-
- Sakaki M, Oka N, Nakanishi R, Yamaguchi K, Fukumori T, Kanayama HO. Serum level of galectin-3 in human bladder cancer. The journal of medical investigation. 2008;55:127–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

