Biofilm streamers cause catastrophic disruption of flow with consequences for environmental and medical systems
- PMID: 23401501
- PMCID: PMC3600445
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1300321110
Biofilm streamers cause catastrophic disruption of flow with consequences for environmental and medical systems
Abstract
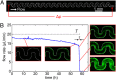
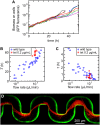
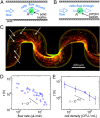
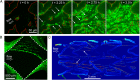
Biofilms are antibiotic-resistant, sessile bacterial communities that occupy most moist surfaces on Earth and cause chronic and medical device-associated infections. Despite their importance, basic information about biofilm dynamics in common ecological environments is lacking. Here, we demonstrate that flow through soil-like porous materials, industrial filters, and medical stents dramatically modifies the morphology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to form 3D streamers, which, over time, bridge the spaces between obstacles and corners in nonuniform environments. We discovered that accumulation of surface-attached biofilm has little effect on flow through such environments, whereas biofilm streamers cause sudden and rapid clogging. We demonstrate that flow-induced shedding of extracellular matrix from surface-attached biofilms generates a sieve-like network that captures cells and other biomass, which add to the existing network, causing exponentially fast clogging independent of growth. These results suggest that biofilm streamers are ubiquitous in nature and strongly affect flow through porous materials in environmental, industrial, and medical systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hall-Stoodley L, et al. Towards diagnostic guidelines for biofilm-associated infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012;65(2):127–145. - PubMed
-
- Kolter R, Greenberg EP. Microbial sciences: The superficial life of microbes. Nature. 2006;441(7091):300–302. - PubMed
-
- Branda SS, Vik S, Friedman L, Kolter R. Biofilms: The matrix revisited. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13(1):20–26. - PubMed
-
- Flemming H-C, Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(9):623–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

