Alternative erythropoietin-mediated signaling prevents secondary microvascular thrombosis and inflammation within cutaneous burns
- PMID: 23401545
- PMCID: PMC3587271
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1214099110
Alternative erythropoietin-mediated signaling prevents secondary microvascular thrombosis and inflammation within cutaneous burns
Abstract
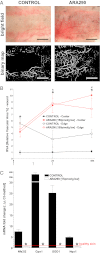
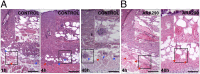
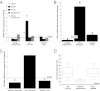
Alternate erythropoietin (EPO)-mediated signaling via the heteromeric receptor composed of the EPO receptor and the β-common receptor (CD131) exerts the tissue-protective actions of EPO in various types of injuries. Herein we investigated the effects of the EPO derivative helix beta surface peptide (synonym: ARA290), which specifically triggers alternate EPO-mediated signaling, but does not bind the erythropoietic EPO receptor homodimer, on the progression of secondary tissue damage following cutaneous burns. For this purpose, a deep partial thickness cutaneous burn injury was applied on the back of mice, followed by systemic administration of vehicle or ARA290 at 1, 12, and 24 h postburn. With vehicle-only treatment, wounds exhibited secondary microvascular thrombosis within 24 h postburn, and subsequent necrosis of the surrounding tissue, thus converting to a full-thickness injury within 48 h. On the other hand, when ARA290 was systemically administered, patency of the microvasculature was maintained. Furthermore, ARA290 mitigated the innate inflammatory response, most notably tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated signaling. These findings correlated with long-term recovery of initially injured yet viable tissue components. In conclusion, ARA290 may be a promising therapeutic approach to prevent the conversion of partial- to full-thickness burn injuries. In a clinical setting, the decrease in burn depth and area would likely reduce the necessity for extensive surgical debridement as well as secondary wound closure by means of skin grafting. This use of ARA290 is consistent with its tissue-protective properties previously reported in other models of injury, such as myocardial infarction and hemorrhagic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.B. and A.C. are officers of Araim Pharmaceuticals and currently hold stock in the company.
Figures

References
-
- Lawrence JW, Mason ST, Schomer K, Klein MB. Epidemiology and impact of scarring after burn injury: A systematic review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2012;33(1):136–146. - PubMed
-
- Stroncek JD, Reichert WM. Overview of wound healing in different tissue types. In: Reichert WM, editor. Indwelling Neural Implants: Strategies for Contending with the in Vivo Environment. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 2008.
-
- Wilgus TA. Immune cells in the healing skin wound: Influential players at each stage of repair. Pharmacol Res. 2008;58(2):112–116. - PubMed
-
- Singer AJ, et al. Rapid and selective enzymatic debridement of porcine comb burns with bromelain-derived Debrase: Acute-phase preservation of noninjured tissue and zone of stasis. J Burn Care Res. 2010;31(2):304–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

