A metabolomics-based strategy for the quality control of traditional chinese medicine: shengmai injection as a case study
- PMID: 23401718
- PMCID: PMC3562660
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/836179
A metabolomics-based strategy for the quality control of traditional chinese medicine: shengmai injection as a case study
Abstract
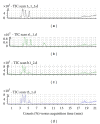
Quality control of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) used clinically is becoming a challenge and has limited the development of TCM due to the high variability in concentration levels of active ingredients and markers as well as the lack of well-established criteria. Using Shengmai injection, which is a well-established TCM, as an example, we developed an integrated profiling approach that simultaneously captures the entire spectrum of ingredients and quantitatively determines the levels of seven key ingredients in the TCM product. A multivariate statistical model was constructed to establish a "seven-marker-" based quality standard that qualified the majority of samples in this study. This newly developed strategy showed that a panel of key ingredients or markers in the TCM product were relatively consistent within a statistically acceptable range. Therefore, this metabolomics-based approach will complement the current quality control standard using the concentration of several key ingredients or their total content and help improve the consistency and clinic efficacy of TCM products.
Figures




References
-
- Gilbert N. Chinese Herbal Medicine Breaks into EU Market. 2012.
-
- Mahady GB, Fong HS, Farnsworth NR. Botanical Dietary Supplements: Quality, Safety, and Efficacy. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Swets & Zeitlinger; 2001.
-
- Di X, Chan KKC, Leung HW, Huie CW. Fingerprint profiling of acid hydrolyzates of polysaccharides extracted from the fruiting bodies and spores of Lingzhi by high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A. 2003;1018(1):85–95. - PubMed
-
- FDA Guidance for Industry—Botanical Drug Products (Draft Guidance) Rockville, Md, USA: US Food and Drug Administration; 2000.
-
- Note for Guidance on Quality, of Herbal Medicinal Products. London, UK: European Medicines Agency; 2001.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

