Nuclear Factor I genomic binding associates with chromatin boundaries
- PMID: 23402308
- PMCID: PMC3610271
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-99
Nuclear Factor I genomic binding associates with chromatin boundaries
Abstract
Background: The Nuclear Factor I (NFI) family of DNA binding proteins (also called CCAAT box transcription factors or CTF) is involved in both DNA replication and gene expression regulation. Using chromatin immuno-precipitation and high throughput sequencing (ChIP-Seq), we performed a genome-wide mapping of NFI DNA binding sites in primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
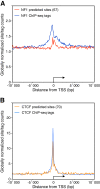
Results: We found that in vivo and in vitro NFI DNA binding specificities are indistinguishable, as in vivo ChIP-Seq NFI binding sites matched predictions based on previously established position weight matrix models of its in vitro binding specificity. Combining ChIP-Seq with mRNA profiling data, we found that NFI preferentially associates with highly expressed genes that it up-regulates, while binding sites were under-represented at expressed but unregulated genes. Genomic binding also correlated with markers of transcribed genes such as histone modifications H3K4me3 and H3K36me3, even outside of annotated transcribed loci, implying NFI in the control of the deposition of these modifications. Positional correlation between + and - strand ChIP-Seq tags revealed that, in contrast to other transcription factors, NFI associates with a nucleosomal length of cleavage-resistant DNA, suggesting an interaction with positioned nucleosomes. In addition, NFI binding prominently occurred at boundaries displaying discontinuities in histone modifications specific of expressed and silent chromatin, such as loci submitted to parental allele-specific imprinted expression.
Conclusions: Our data thus suggest that NFI nucleosomal interaction may contribute to the partitioning of distinct chromatin domains and to epigenetic gene expression regulation.NFI ChIP-Seq and input control DNA data were deposited at Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) repository under accession number GSE15844. Gene expression microarray data for mouse embryonic fibroblasts are on GEO accession number GSE15871.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global mapping of cell type-specific open chromatin by FAIRE-seq reveals the regulatory role of the NFI family in adipocyte differentiation.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002311. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22028663 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor I revealed as family of promoter binding transcription activators.BMC Genomics. 2011 Apr 7;12:181. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-181. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21473784 Free PMC article.
-
The hormone responsive region of mouse mammary tumor virus positions a nucleosome and precludes access of nuclear factor I to the promoter.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;57(1-2):19-31. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(96)00262-2. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8645614
-
[Transcription factors of the nuclear factor 1 (NF1) family. Role in chromatin remodelation].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2008 May-Jun;42(3):388-404. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2008. PMID: 18702298 Review. Russian.
-
Chromatin structure and the regulation of gene expression: remodeling at the MMTV promoter.J Mol Med (Berl). 1996 Dec;74(12):711-24. doi: 10.1007/s001090050076. J Mol Med (Berl). 1996. PMID: 8974015 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the genetics and mechanisms of predisposition to multiple myeloma.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 5;15(1):6644. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50932-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39103364 Free PMC article.
-
Overgrowth-intellectual disability disorders: progress in biology, patient advocacy and innovative therapies.Dis Model Mech. 2025 May 1;18(5):dmm052300. doi: 10.1242/dmm.052300. Epub 2025 May 12. Dis Model Mech. 2025. PMID: 40353642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFI transcription factors provide chromatin access to maintain stem cell identity while preventing unintended lineage fate choices.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Jun;22(6):640-650. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0513-0. Epub 2020 May 11. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32393888 Free PMC article.
-
Differential DNA methylation of vocal and facial anatomy genes in modern humans.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 4;11(1):1189. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15020-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32132541 Free PMC article.
-
Positional plasticity in regenerating Amybstoma mexicanum limbs is associated with cell proliferation and pathways of cellular differentiation.BMC Dev Biol. 2015 Nov 23;15:45. doi: 10.1186/s12861-015-0095-4. BMC Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26597593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen M, Mermod N, Horwitz MS. Protein-protein interactions between adenovirus DNA polymerase and nuclear factor I mediate formation of the DNA replication preinitiation complex. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(30):18634–18642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

