A synergistic interaction between transcription factors nuclear factor-κB and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 23402362
- PMCID: PMC3583822
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-29
A synergistic interaction between transcription factors nuclear factor-κB and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion
Abstract
Background: The transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) has been implicated in gastric cancer metastasis, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated the role of the interaction between NF-κB and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) in controlling metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells.
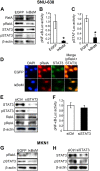
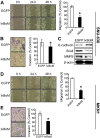
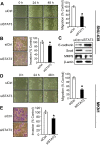
Methods: Immunohistochemistry for NF-κB p65 (RelA), phospho-Tyr705-STAT3 (pSTAT3), or matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) was performed on tissue array slides containing 255 gastric carcinoma specimens. NF-κB inhibition in SNU-638 and MKN1 gastric cancer cell lines were performed by transduction with a retroviral vector containing NF-κB repressor mutant of IκBα, and STAT3 was silenced by RNA interference. We also did luciferase reporter assay, double immunofluorescence staining and immunoblotting. Cell migration and invasion were determined by wound-healing assay and invasion assay, respectively.
Results: NF-κB and STAT3 were constitutively activated and were positively correlated (P=0.038) in gastric cancer tissue specimens. In cell culture experiments, NF-κB inhibition reduced STAT3 expression and activation, whereas STAT3 silencing did not affect NF-κB activation. Moreover, both NF-κB inhibition and STAT3 silencing decreased gastric cancer cell migration and invasion in a synergistic manner. In addition, both NF-κB activation and STAT3 activation were positively correlated with MMP9 in gastric cancer tissues (P=0.001 and P=0.022, respectively), decreased E-cadherin expression and increased Snail and MMP9 expressions in cultured cells.
Conclusion: NF-κB and STAT3 are positively associated and synergistically contribute to the metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells. Thus, dual use of NF-κB and STAT3 inhibitors may enhance the efficacy of the anti-metastatic treatment of gastric cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3-induced metastatic potential in gastric cancer cells is enhanced by glycogen synthase kinase-3β.APMIS. 2015 May;123(5):373-82. doi: 10.1111/apm.12370. Epub 2015 Apr 4. APMIS. 2015. PMID: 25846563
-
A hypoxia-dependent upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by nuclear factor-κB promotes gastric tumour growth and angiogenesis.Br J Cancer. 2011 Jan 4;104(1):166-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606020. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21119667 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB activation correlates with better prognosis and Akt activation in human gastric cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;11(7):2518-25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1282. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15814628
-
NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer.Protein Cell. 2013 Mar;4(3):176-85. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-2084-3. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23483479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010 Feb;21(1):11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.11.005. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010. PMID: 20018552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signalling via Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in ovarian cancer.Br J Cancer. 2014 Jan 7;110(1):133-45. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.673. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24220695 Free PMC article.
-
rs744166 polymorphism of the STAT3 gene is associated with risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:527918. doi: 10.1155/2014/527918. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24864251 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Signaling in Gastric Cancer.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Mar 28;9(4):119. doi: 10.3390/toxins9040119. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28350359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of FOXO1 promotes gastric tumour growth and metastasis through upregulation of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2/neu expression.Br J Cancer. 2015 Oct 20;113(8):1186-96. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.273. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26448177 Free PMC article.
-
RBBP6, a RING finger-domain E3 ubiquitin ligase, induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Nov 4;10(11):833. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2070-7. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31685801 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

