Nanoparticle geometry and surface orientation influence mode of cellular uptake
- PMID: 23402533
- PMCID: PMC3860363
- DOI: 10.1021/nn304439f
Nanoparticle geometry and surface orientation influence mode of cellular uptake
Abstract
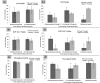
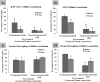
In order to engineer safer nanomaterials, there is a need to understand, systematically evaluate, and develop constructs with appropriate cellular uptake and intracellular fates. The overall goal of this project is to determine the uptake patterns of silica nanoparticle geometries in model cells, in order to aid in the identification of the role of geometry on cellular uptake and transport. In our experiments we observed a significant difference in the viability of two phenotypes of primary macrophages; immortalized macrophages exhibited similar patterns. However, both primary and immortalized epithelial cells did not exhibit toxicity profiles. Interestingly uptake of these geometries in all cell lines exhibited very different time-dependent patterns. A screening of a series of chemical inhibitors of endocytosis was performed to isolate the uptake mechanisms of the different particles. The results show that all geometries exhibit very different uptake profiles and that this may be due to the orientation of the nanoparticles when they interact with the cell surface. Additionally, evidence suggests that these uptake patterns initialize different downstream cellular pathways, dependent on cell type and phenotype.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Organically Modified Silica Nanoparticles Interaction with Macrophage Cells: Assessment of Cell Viability on the Basis of Physicochemical Properties.J Pharm Sci. 2015 Nov;104(11):3943-3951. doi: 10.1002/jps.24614. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26295279
-
Size of submicrometric and nanometric particles affect cellular uptake and biological activity of macrophages in vitro.Inhal Toxicol. 2012 Aug;24(9):580-8. doi: 10.3109/08958378.2012.699984. Inhal Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22861001
-
Silica-Based Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: From Nanocarriers to Biomodulators.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Aug 18;53(8):1545-1556. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00280. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 32667182
-
Differential cytotoxic and inflammatory potency of amorphous silicon dioxide nanoparticles of similar size in multiple cell lines.Nanotoxicology. 2017 Mar;11(2):223-235. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2017.1287313. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Nanotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 28142331
-
Effects of the presence or absence of a protein corona on silica nanoparticle uptake and impact on cells.ACS Nano. 2012 Jul 24;6(7):5845-57. doi: 10.1021/nn300223w. Epub 2012 Jun 29. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 22721453
Cited by
-
Hyperspectral dark field optical microscopy for orientational imaging of a single plasmonic nanocube using a physics-based learning method.Nanoscale Adv. 2022 Aug 24;4(19):4094-4101. doi: 10.1039/d2na00469k. eCollection 2022 Sep 27. Nanoscale Adv. 2022. PMID: 36285219 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence and Utility of Nonspherical Particles in Biomedicine.Ind Eng Chem Res. 2015 Apr 29;54(16):4043-4059. doi: 10.1021/ie504452j. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 27182109 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Mangostin-Loaded Transferrin-Conjugated Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles: Development and Characterization for Tumor-Targeted Delivery.ScientificWorldJournal. 2022 Aug 30;2022:9217268. doi: 10.1155/2022/9217268. eCollection 2022. ScientificWorldJournal. 2022. PMID: 36081606 Free PMC article.
-
Missing-in-metastasis protein promotes internalization of magnetic nanoparticles via association with clathrin light chain and Rab7.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019 Feb;1863(2):502-510. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019. PMID: 30528490 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of polyplex morphology on cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and transgene expression.ACS Nano. 2013 Dec 23;7(12):10612-20. doi: 10.1021/nn403069n. Epub 2013 Nov 13. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 24195594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nel AE, Madler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EM, Somasundaran P, Klaessig F, Castranova V, Thompson M. Understanding Biophysicochemical Interactions at the Nano-Bio Interface. Nat Mater. 2009;8:543–557. - PubMed
-
- Jones AT, Gumbleton M, Duncan R. Understanding Endocytic Pathways and Intracellular Trafficking: A Prerequisite for Effective Design of Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2003;55:1353–1357. - PubMed
-
- Pelkmans L, Burli T, Zerial M, Helenius A. Caveolin-Stabilized Membrane Domains as Multifunctional Transport and Sorting Devices in Endocytic Membrane Traffic. Cell. 2004;118:767–780. - PubMed
-
- Wiewrodt R, Thomas AP, Cipelletti L, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Weitz DA, Feinstein SI, Schaffer D, Albelda SM, Koval M, Muzykantov VR. Size-Dependent Intracellular Immunotargeting of Therapeutic Cargoes into Endothelial Cells. Blood. 2002;99:912–922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

