Cancer prevention by tocopherols and tea polyphenols
- PMID: 23403075
- PMCID: PMC3713114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.051
Cancer prevention by tocopherols and tea polyphenols
Abstract
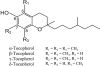
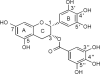
Tocopherols (vitamin E) and tea polyphenols have been reported to have cancer preventive activities. Large-scale human trials with high doses of alpha-tocopherol, however, have produced disappointing results. This review presents data showing that - and -tocopherols inhibit colon, lung, mammary and prostate carcinogenesis in animal models, whereas -tocopherol is ineffective in animal and human studies. Possible mechanisms of action are discussed. A broad cancer preventive activity of green tea polyphenols has been demonstrated in animal models, and many mechanisms have been proposed. The cancer preventive activity of green tea in humans, however, has not been conclusively demonstrated and remains to be further investigated.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Traber MG, Vitamin E. In: Present Knowledge in Nutrition. 9th Edition Bowman BA, Russell RM, editors. ILSI Press; Washington DC: 2006. pp. 211–219.
-
- Patel A, Liebner F, Netscher T, Mereiter K, Rosenau T. Vitamin E chemistry. Nitration of non-alpha-tocopherols: products and mechanistic considerations. J Org Chem. 2007;72:6504–6512. - PubMed
-
- Lee IM, Cook NR, Gaziano JM, Gordon D, Ridker PM, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Buring JE. Vitamin E in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: the Women's Health Study: a randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2005;294:56–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases