Survival and cure trends for European children, adolescents and young adults diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from 1982 to 2002
- PMID: 23403323
- PMCID: PMC3640119
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2012.071597
Survival and cure trends for European children, adolescents and young adults diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from 1982 to 2002
Abstract
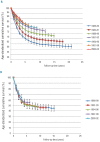
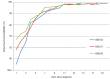
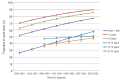
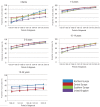
Proportion cured is a potentially more informative cancer outcome measurement than 5-year survival. We present population-based estimates of cure for young patients diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Europe from 1982 to 2002. Thirty-five European cancer registries provided data. Survival was estimated by age, period of diagnosis and European region, and used as input for parametric cure models, which assume cured patients have the same mortality as the general population. For acute lymphoblastic leukemia diagnosed in 1-14 year olds in 2000-2002, over 77% were estimated cured. The proportion cured improved significantly over the study period: an impressive 26-58% in infants (up to 1 year), 70-90% in 1-4 year olds, 63-86% in 5-9 year olds, 52-77% in 10-14 year olds, and 44-50% in 15-24 year olds. Regional variations in proportion cured reduced over time for 1-14 year-olds, but persisted in infants and 15-24 year olds. Five-year survival was always slightly higher than proportion cured. Considerable proportions of young patients were estimated cured of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nevertheless, a small excess risk of death persisted beyond five years after diagnosis when patients remained at risk for late treatment effects, late relapses and second primaries.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cure trends in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: is it time for a revised concept of cure?Haematologica. 2013 May;98(5):655-6. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.084269. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 23633537 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coebergh JW, Reedijk AM, de Vries E, Martos C, Jakab Z, Steliarova-Foucher E, et al. Leukaemia incidence and survival in children and adolescents in Europe 1978–1997. Report from the Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(13):2019–36 - PubMed
-
- Gatta G, Zigon G, Capocaccia R, Coebergh JW, Desandes E, Kaatsch P, et al. Survival of European children and young adults with cancer diagnosed 1995–2002. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(6):992–1005 - PubMed
-
- Brandwein JM. Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adolescents and Young Adults. Curr Oncol Rep. 2011;13(5): 371–8 - PubMed
-
- Brenner H, Coebergh JW, Parkin DM, Izarzugaza I, Clavel J, Arndt V, et al. Up-to-date monitoring of childhood cancer long-term survival in Europe: leukaemias and lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(9):1569–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

