A reprofiled drug, auranofin, is effective against metronidazole-resistant Giardia lamblia
- PMID: 23403423
- PMCID: PMC3632933
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01675-12
A reprofiled drug, auranofin, is effective against metronidazole-resistant Giardia lamblia
Abstract
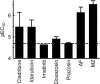
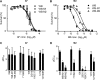
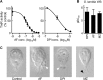
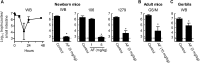
Giardiasis is one of the most common causes of diarrheal disease worldwide. Treatment is primarily with 5-nitro antimicrobials, particularly metronidazole. Resistance to metronidazole has been described, and treatment failures can occur in up to 20% of cases, making development of alternative antigiardials an important goal. To this end, we have screened a chemical library of 746 approved human drugs and 164 additional bioactive compounds for activity against Giardia lamblia. We identified 56 compounds that caused significant inhibition of G. lamblia growth and attachment. Of these, 15 were previously reported to have antigiardial activity, 20 were bioactive but not approved for human use, and 21 were drugs approved for human use for other indications. One notable compound of the last group was the antirheumatic drug auranofin. Further testing revealed that auranofin was active in the low (4 to 6)-micromolar range against a range of divergent G. lamblia isolates representing both human-pathogenic assemblages A and B. Most importantly, auranofin was active against multiple metronidazole-resistant strains. Mechanistically, auranofin blocked the activity of giardial thioredoxin oxidoreductase, a critical enzyme involved in maintaining normal protein function and combating oxidative damage, suggesting that this inhibition contributes to the antigiardial activity. Furthermore, auranofin was efficacious in vivo, as it eradicated infection with different G. lamblia isolates in different rodent models. These results indicate that the approved human drug auranofin could be developed as a novel agent in the armamentarium of antigiardial drugs, particularly against metronidazole-resistant strains.
Figures
References
-
- Savioli L, Smith H, Thompson A. 2006. Giardia and Cryptosporidium join the ‘Neglected Diseases Initiative’. Trends Parasitol. 22:203–208 - PubMed
-
- Wensaas KA, Langeland N, Hanevik K, Morch K, Eide GE, Rortveit G. 2012. Irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue 3 years after acute giardiasis: historic cohort study. Gut 61:214–219 - PubMed
-
- Escobedo AA, Cimerman S. 2007. Giardiasis: a pharmacotherapy review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother 8:1885–1902 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

